Developer Console and Adobe I/O CLI for Cloud Manager to Debug AEM as a Cloud Service (AEMaaCS)
AEM as a Cloud Service provides a Developer Console for each environment that exposes various details of the running AEM service that are helpful in debugging. Each AEM as a Cloud Service environment has its own Developer Console.
Adobe I/O CLI for Cloud Manager provides commands to download/tail the logs from AEM as a Cloud Service environment.
Some of the below Adobe documents provides the required details on this topic, thought of sharing my learning for reference
Debugging AEM as a Cloud Service | Adobe Experience Manager
The Developer console can be accessed through Cloud Manager or Adobe I/O CLI for Cloud Manager
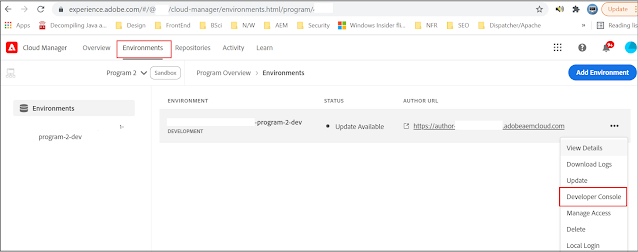
Log in to CM, select the appropriate Program(Select the Program enabled for AEM as a Cloud - the AMS customers participating in AEM as a Cloud will have two different programs)
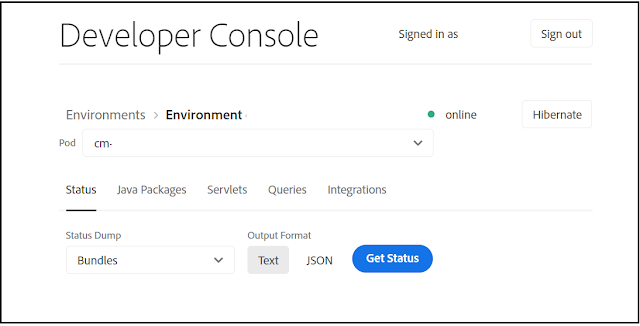
Click on the three dots for the specific environment, and select “Developer Console”, the same can be accessed through the Environment tab. You will be able to see the Developer Console with the environment details.
Change the value in the pod dropdown list to view the different server details on the environment.
To access and use the Developer Consol, the developer must be a member of the Cloud Manager Product’s Developer - Cloud Service Product Profile. Also, the developer must be a member of the AEM Users or AEM Administrators Product Profile on AEM Author and/or Publish. The exception being for Sandbox Programs, where any user with access to the Cloud Manager Sandbox Program will have access to Developer Console.
The Developer Console provides similar information as the AEM SDK’s local quickstart’s OSGi Web console, with the marked difference that the Developer Console is read-only.
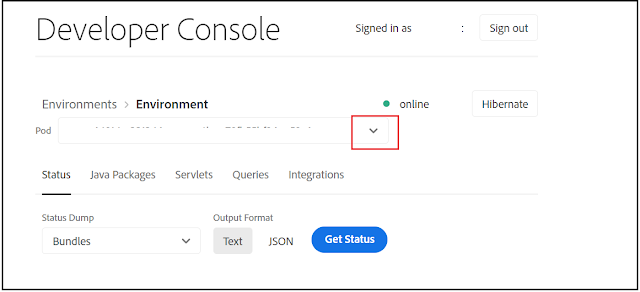
As illustrated above, available statuses information includes the state of bundles, components, OSGI configurations, oak indexes, OSGI services, and Sling jobs.
Also, the Query Performance tool can be accessed from the Queries tab - /libs/granite/operations/content/diagnosistools/queryPerformance.html.
Sandbox Program environments enter a hibernation mode if no activity is detected for a certain period of time. Hibernation is unique to Sandbox Program environments. Production program environments do not hibernate.
Hibernation is categorized as:
Automatic Sandbox Program environments are automatically hibernated after eight hours of inactivity, meaning that neither the author nor preview or publish services receive requests.
Manual: As a user, you may manually hibernate a Sandbox Program environment, although there is no requirement to do so since hibernation will occur automatically after a certain period (eight hours) of inactivity.
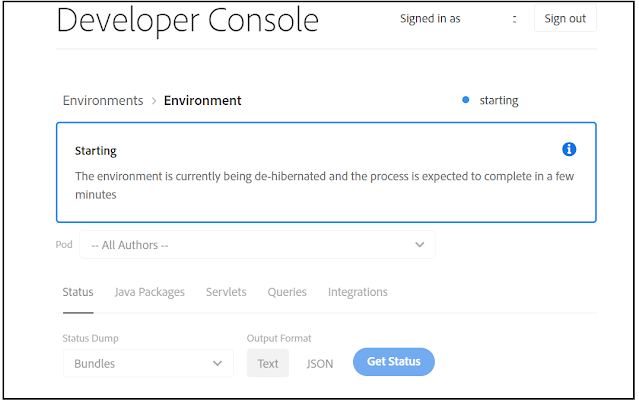
You will see the below screen if the Sandbox environment is Hibernated while accessing the instances
The Environment can be De-Hibernated through Developer Console
The Developer Console can be also accessed through Adobe I/O CLI for Cloud Manager
aio cloudmanager:open-developer-console <ENVIRONMENTID> --programId <PROGRAMID>
The Environment ID and Program ID can be retrieved by accessing the environment through Cloud Manager.
The Program and Environment ID's can be also retrieved through Adobe I/O CLI for Cloud Manager
npm install -g @adobe/aio-cli
aio plugins:install @adobe/aio-cli-plugin-cloudmanager
aio auth:login
aio cloudmanager:org:select
aio cloudmanager:list-programs
aio config:set cloudmanager_programid <<Program ID>>
aio cloudmanager:list-environments
Executing the below command opens the Developer Console
aio cloudmanager:open-developer-console <ENVIRONMENTID> --programId <PROGRAMID>
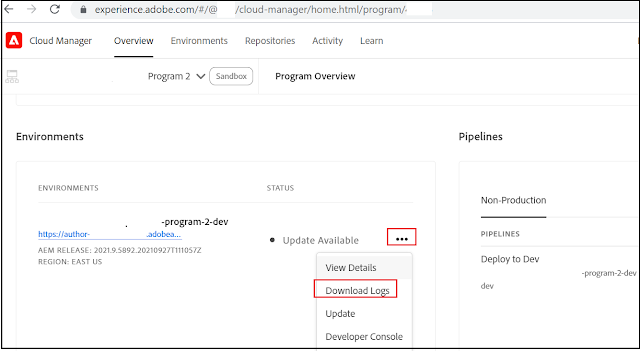
The AEM server logs can also be accessed through Cloud Manager or Adobe I/O CLI for Cloud Manager
Logs can be tailed/downloaded through CLI commands
aio cloudmanager:environment:list-available-log-options <<Environment ID>> - this will list out all the avilable log services and names
aio cloudmanager:environment:download-logs <<Environment ID>> <<Service>> <<Name>> [Number of days-default 1]
aio cloudmanager:environment:download-logs 22222 author aemerror 2
This will download the log file to the current folder - use the command parameters to change the location if required
aio cloudmanager:environment:download-logs 22222 dispatcher aemdispatcher --outputDirectory=C:\test
The log can be tailed if required
aio cloudmanager:environment:tail-log <<Environment ID>> <<Service>> <<Name>>
aio cloudmanager:environment:tail-log 22222 author aemerror
The CRXDE Lite is only accessible on Local SDK instances and AEM as a Cloud Service Development environments but not available on Stage or Production environments.
Deployed OSGi configurations cannot be reviewed via CRXDE Lite. OSGi configurations are maintained in the AEM Project’s ui.apps code package at /apps/example/config.xxx, however upon deployment to AEM as a Cloud Service environments, the OSGi configurations resources are not persisted to the JCR, therefore not visible via CRXDE Lite. The OSGI configurations can be reviewed through the Developer console.
Oservervation while using the Adobe I/O CLI - I was getting 401 Unautorized exception while executing the CLI command, even aio auth:login not helped, the issue is resolved first by clearing the configurations(aio config:clear) then execute the aio auth:login and other commands