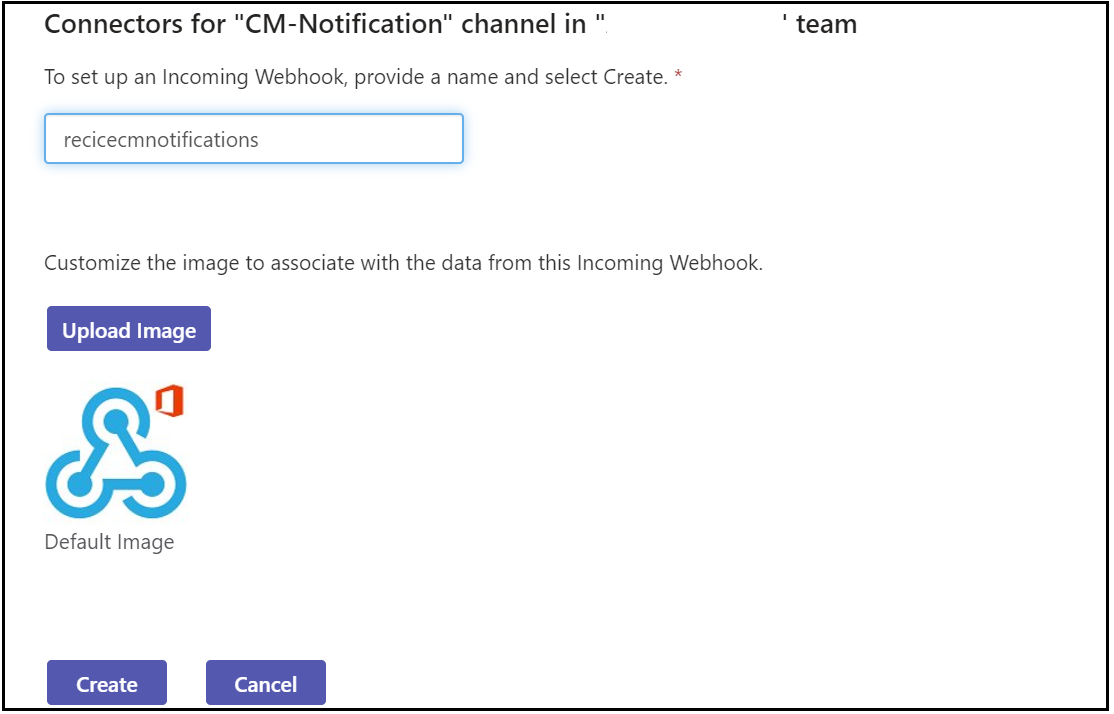
The AEM Project Archetype includes an optional, dedicated front-end build mechanism based on Webpack. The ui.frontend module is the central location for all of the project’s front-end resources including JavaScript and CSS files. The client library is generated through aem-clientlib-generator npm module and placed under ui.apps module during the build process.
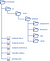
The current module structure shown below supports the front-end components for single-tenant/theme, the module can be duplicated to support multiple tenants but that will create constraints to manage also impact the overall deployment timeline.
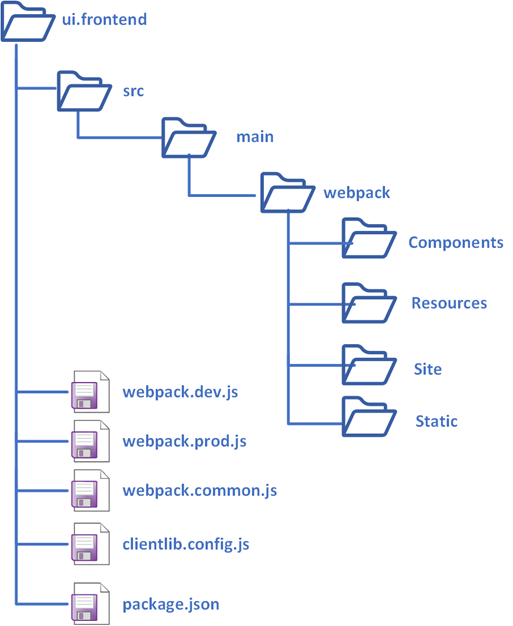
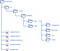
In this tutorial let us see how to enable the front end module to support multiple tenants/themes. The new module structure is as below.
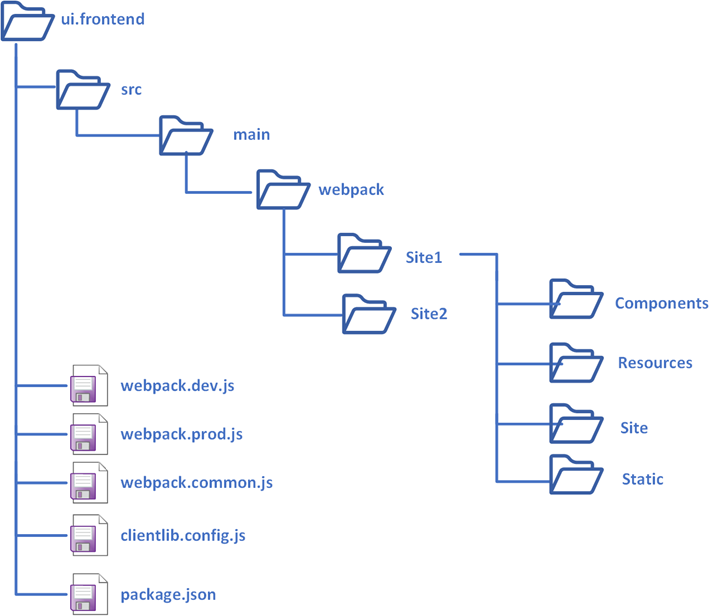
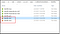
The final client libraries are generated in the below structure
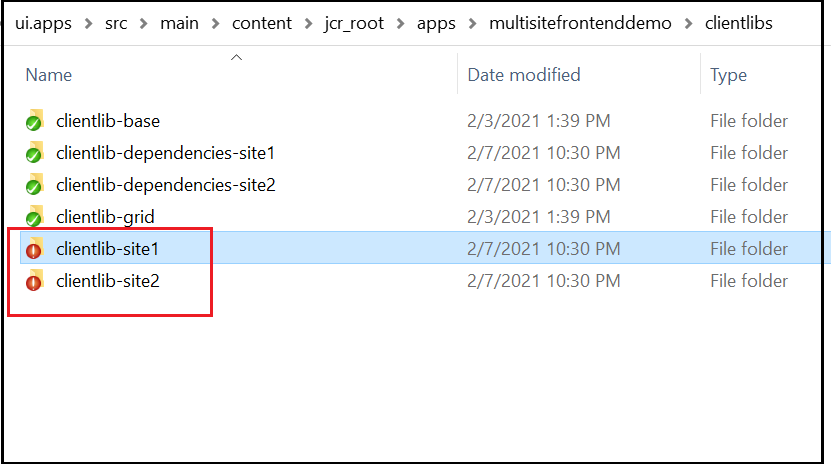
Create the theme/tenant specific folders under (copy the default content under webpack to the site-specific folders)
/ui.frontend/src/main/webpack/site1, /ui.frontend/src/main/webpack/site2 etc
webpack.common.js
The default webpack.common.js is enabled to support a single entry(tenant), enable the required configurations to support additional tenants(e.g site1, site2, etc)
...
const SITE_1='/site1';
const SITE_2='/site2';...entry: {
site1: SOURCE_ROOT + SITE_1 +'/site/main.ts',
site2: SOURCE_ROOT + SITE_2 +'/site/main.ts'
},output: {
filename: (chunkData) => {
return chunkData.chunk.name === 'dependencies' ? 'clientlib-dependencies/[name].js' : 'clientlib-[name]/[name].js'; }...plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin(),
new webpack.NoEmitOnErrorsPlugin(),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: 'clientlib-[name]/[name].css'
}),
new CopyWebpackPlugin([
{ from: path.resolve(__dirname, SOURCE_ROOT + SITE_1 +'/resources/'), to: './clientlib-site1'},
{from: path.resolve(__dirname, SOURCE_ROOT + SITE_2 +'/resources/'), to: './clientlib-site2'}
])
]
webpack.dev.js
Enable the static HTML for testing different sites through webpack server by default the configurations are enabled to support a single tenant.
...plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
inject: true,
template: path.resolve(__dirname, SOURCE_ROOT + '/site1/static/index.html'),
filename: 'site1.html',
chunks: ['site1']
}),
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
inject: true,
template: path.resolve(__dirname, SOURCE_ROOT + '/site2/static/index.html'),
filename: 'site2.html',
chunks: ['site2']
})
]
...
clientlib.config.js
Enable the required configurations to generate the client library for different websites — site1.site, site1.dependencies, site2.site, site2.dependencies, etc
//site1
...
{
...libsBaseConfig,
name: 'clientlib-site1',
categories: ['site1.site'],
dependencies: ['site1.dependencies'],
assets: {
// Copy entrypoint scripts and stylesheets into the respective ClientLib
// directories
js: {
cwd: 'clientlib-site1',
files: ['**/*.js'],
flatten: false
},
css: {
cwd: 'clientlib-site1',
files: ['**/*.css'],
flatten: false
},// Copy all other files into the `resources` ClientLib directory
resources: {
cwd: 'clientlib-site1',
files: ['**/*.*'],
flatten: false,
ignore: ['**/*.js', '**/*.css']
}
}
}
...//site2
...
{
...libsBaseConfig,
name: 'clientlib-site2',
outputPath: CLIENTLIB_DIR+'/clientlib-site2',
categories: ['site2.site'],
dependencies: ['site2.dependencies'],
assets: {
// Copy entrypoint scripts and stylesheets into the respective ClientLib
// directories
js: {
cwd: 'clientlib-site2',
files: ['**/*.js'],
flatten: false
},
css: {
cwd: 'clientlib-site2',
files: ['**/*.css'],
flatten: false
},// Copy all other files into the `resources` ClientLib directory
resources: {
cwd: 'clientlib-site2',
files: ['**/*.*'],
flatten: false,
ignore: ['**/*.js', '**/*.css']
}
}
}
The default client library path can be overridden using outputPath e.g. outputPath: CLIENTLIB_DIR+’/clientlib-site2'
Now the style for different sites can be tested through a static index.html file
Navigate to ui.frontend and execute npm run startThe site-specific static files can be accessed through
http://localhost:8080/site1.html
http://localhost:8080/site2.htmlThe browser tabs will be reloaded on style/script changes.
The site-specific client libraries can be enabled through editable template policy or through page rendering components.
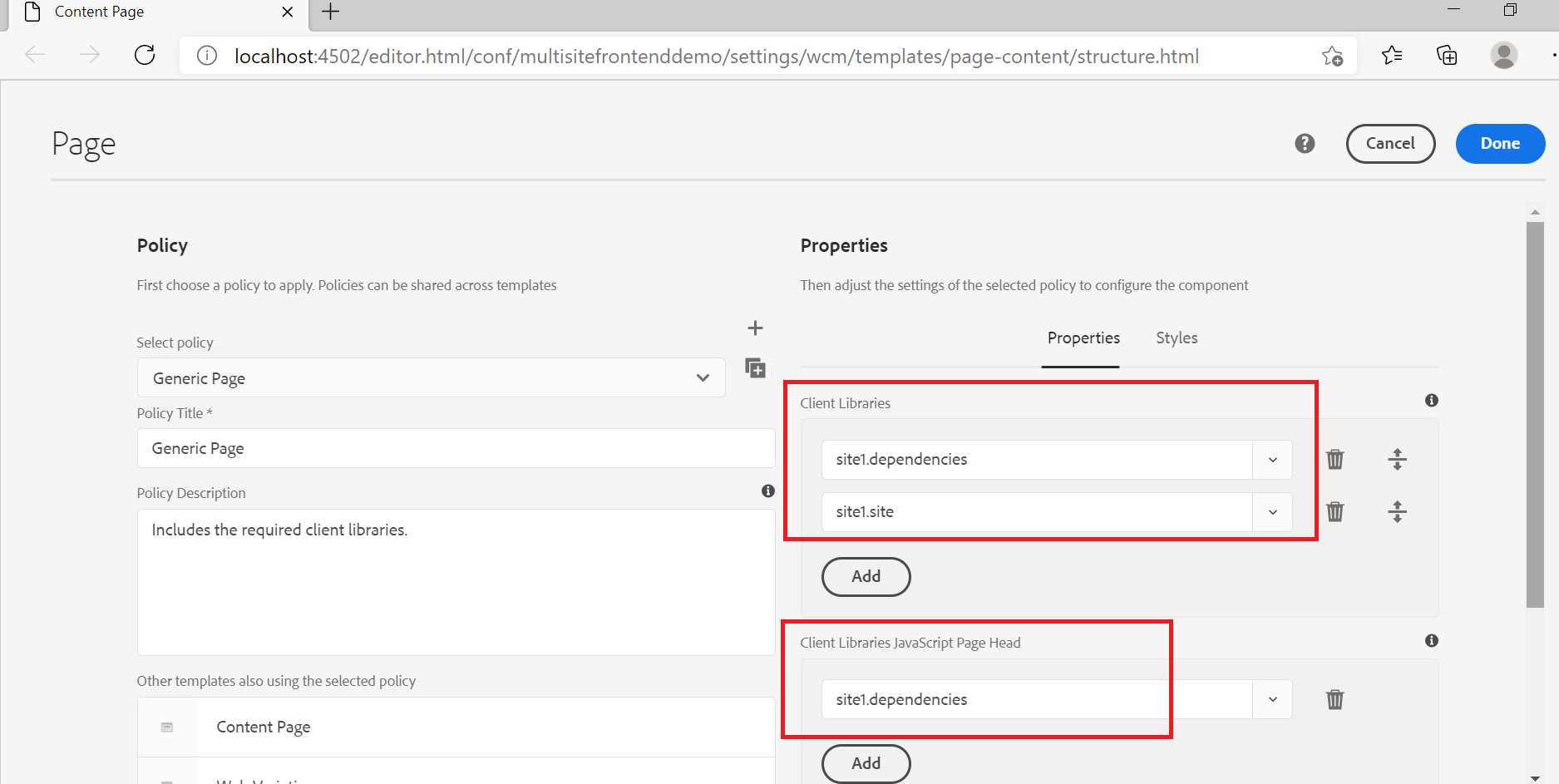
The sample project is also enabled with webpack watch and aemfed to deploy/test the style/script changes quickly.
Navigate to ui.frontend and execute npm run watch
Navigate to ui.frontend in another terminal execute npm run aem-syncNow the AEM pages can be accessed through the proxy — the changes will be synced to AEM and the browser tab reloads, the webpack proxy inject the local CSS and js files to the AEM pages.
http://localhost:3000/content/multisitefrontenddemo/us/en.html
To deploy the final changes to AEM, navigate to project root folder and execute mvn -PautoInstallSinglePackage clean install — compile the front end module and generate the client libraries to ui-apps and deploy the complete package to AEM
The style/scripts specific to multiple tenants can be managed through a single front-end module, the site specific client libraries are generated and deployed through Maven build to the AEM server. The Webpack server, watch, aemsync, browsersync, aemfed tools can be used for testing the frontend changes quickly from the local machine.
Refer to https://github.com/techforum-repo/youttubedata/blob/master/aem/multisitefrontenddemo for sample front end module enabled with multi-site support( demo is built based on archetype 24 and AEM as cloud service SDK).
References: