Tech Mastery: Deep Dives into AEM, Cloud Technologies, AI Innovations, and Advanced Marketing Strate
Welcome to Tech Mastery, your expert source for insights into technology and digital strategy. Explore topics like Adobe Experience Manager, AWS, Azure, generative AI, and advanced marketing strategies. Delve into MACH architecture, Jamstack, modern software practices, DevOps, and SEO. Our blog is ideal for tech professionals and enthusiasts eager to stay ahead in digital innovations, from Content Management to Digital Asset Management and beyond.
Friday, December 11, 2020
Sync External Git Repository to Cloud Manager Repository
Saturday, December 5, 2020
Cloud Manager Notifications to Collaboration Channels — Microsoft Teams
The Cloud Manager CI/CD pipeline executes series of steps to build and deploy the code to AMS and AEM as Cloud AEM platforms, refer to the below video to understand the basics of Cloud Manager.
Cloud manager exposes APIs to interact with the CM settings and to manage the pipeline also emits different events on pipeline execution.
The Adobe I/O along with custom webhooks can be used to receive the appropriate events from Cloud Manager and take the required action. Also, the Cloud Manager APIs can be invoked through Adobe I/O to perform different operations on Cloud Manager.
One of the important requirements while working with Cloud Manager is notifying the developer on the status of pipeline execution, the individual developers can subscribe to the email notification as required but there is no default option to send the notifications to group email or another collaboration channel.
Most of the teams like the notification to the Collaboration Channels e.g Microsoft Teams, the Adobe I/O along with CM API, Events, and Microsoft Teams Webhook can be used to send the Cloud Manager Notification to the Microsoft Teams Channel.
The Microsoft teams or other Collobrarion Tools helps to enable the webhooks(POST with JSON data), the webhook can be used to send the notification to the specific channel.
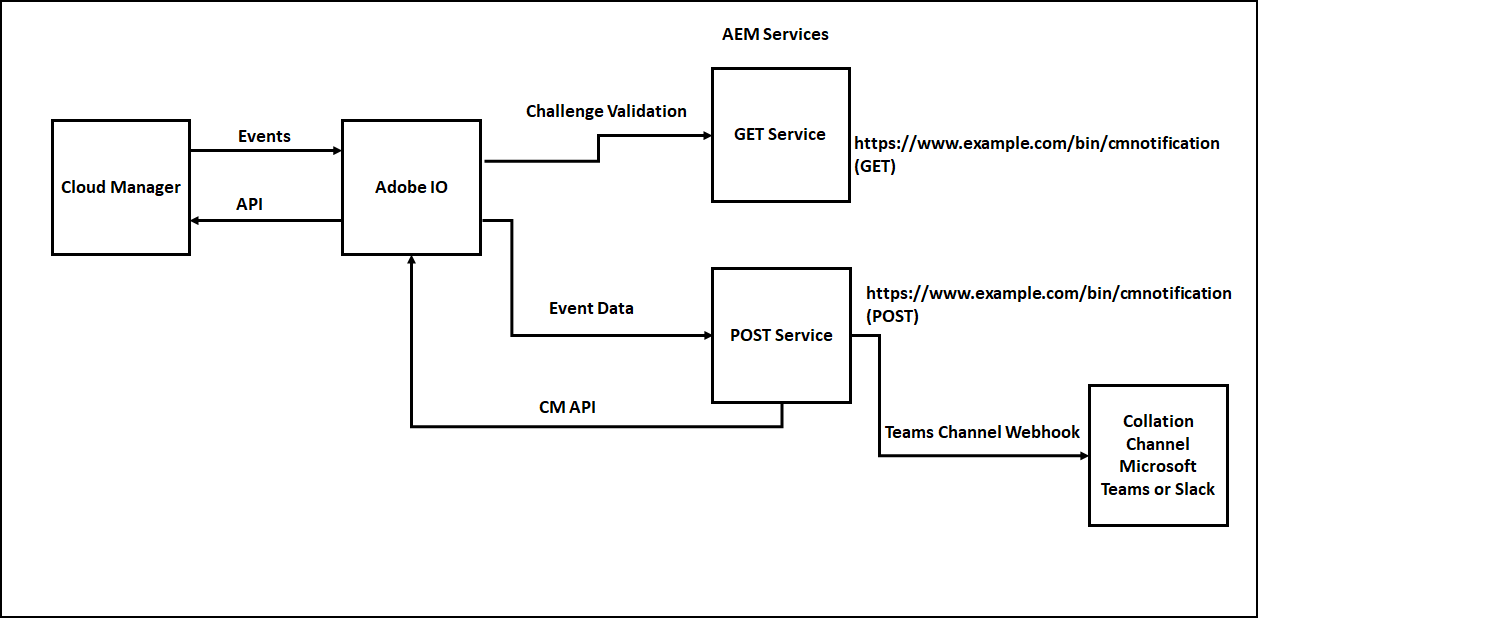
The notification can be managed through a custom webhook or Adobe I/O runtime, Adobe I/O runtime expects two Webhook services to receive the events(due to this the Collaboration Channel Webhook can’t be directly used in Adobe I/O Notification)
- GET service to receive the challenge request and respond to the challenge
- POST service to receive the different event details
The signature validation is performed as part of the POST service to ensure the request is posted only from Adobe I/O and to protect from security issues.
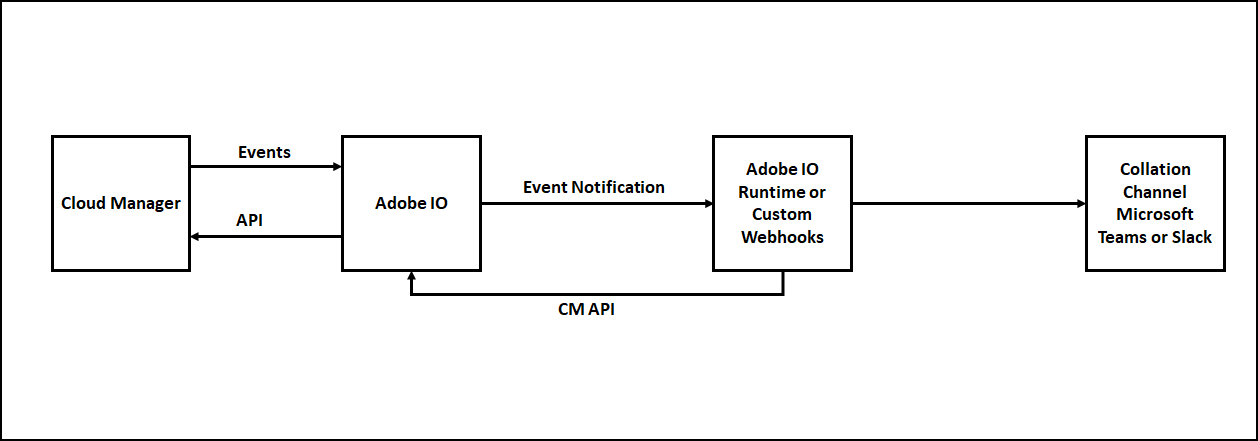
Some of the additional overheads we discussed e.g GET service to handle challenge and signature validation as part of the POST service can be avoided by using Adobe I/O runtime to communicate with the external webhooks.
We can use one of the below option to send the Cloud Manager notifications to the Collaboration Channels e.g. Microsoft Teams
- Enable the Notification through Custom Webhooks hosted on Node JS — Refer Cloud Manager API and Cloud Manager API Tutorial. Somehow the step7-teams.js was failing to create the JWT token with the RS256 algorithm, to fix the issue updated step7-teams.js to use “jsonwebtoken” instead of “jsrsasign” module.
- Enable the Notification through Adobe I/O Runtime — Refer Cloud Manager Meets Jenkins
- Enable the Notification through Custom Webhooks hosted on AEM
Let us now see the details on how to enable the custom webhooks in AEM to send the Cloud Manager pipeline notifications to the Microsoft Teams channel, the same steps can be reused with minimal changes to send the notification to other tools e.g. Slack.
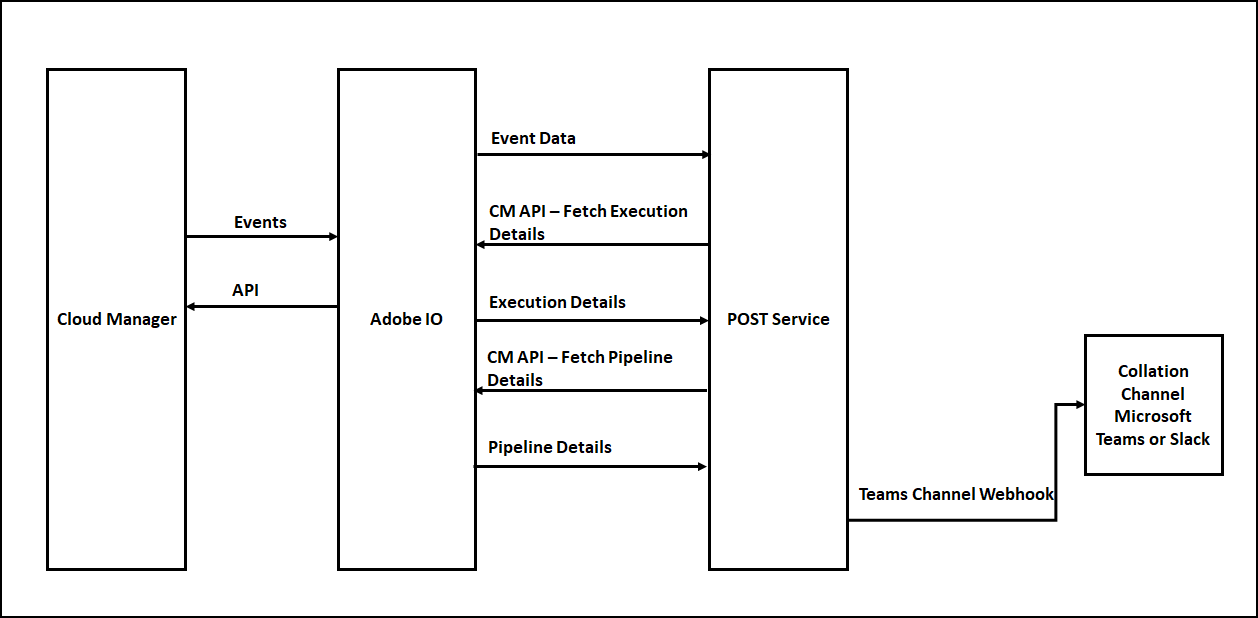
You can get all the required additional data by invoking the CM APIs’s, the Event JSON will have the URLs to get the execution details, execution details subsequently will have the URLs to get the program details, pipeline details, step details, logs, etc(Explore the input JSON’s to get the required details).
Enable Webhook for Teams Channel:
As a first step, let us register the webhooks for the Microsoft Teams channel.
Define a Channel to receive the CM pipeline notifications, Go to the Teams Channel for which the Webhook should be enabled, and click on the three dots in the upper right corner then click on Connectors.
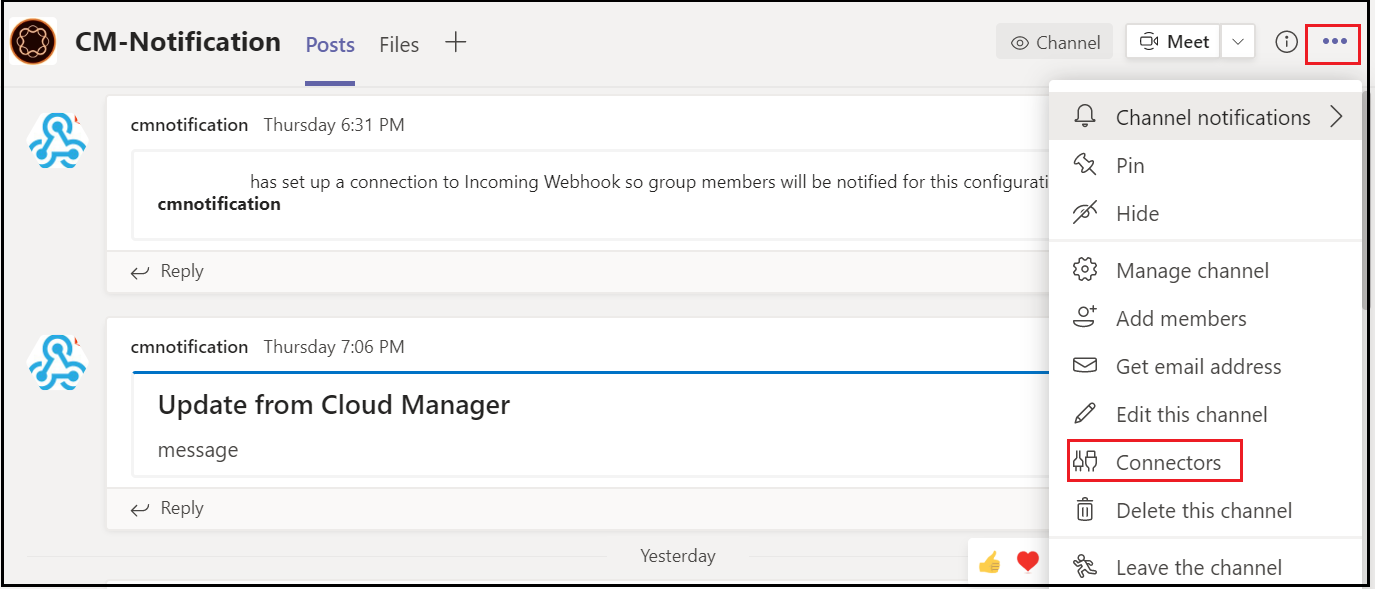
Configure an “Incoming Webhook”
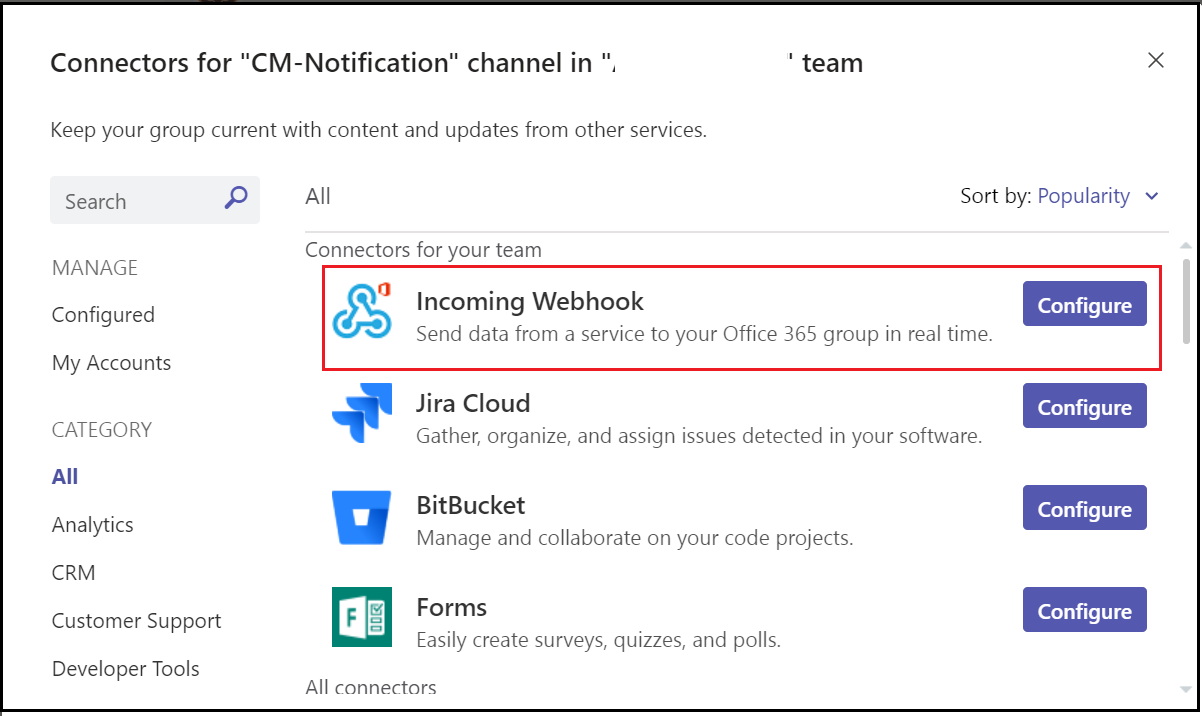
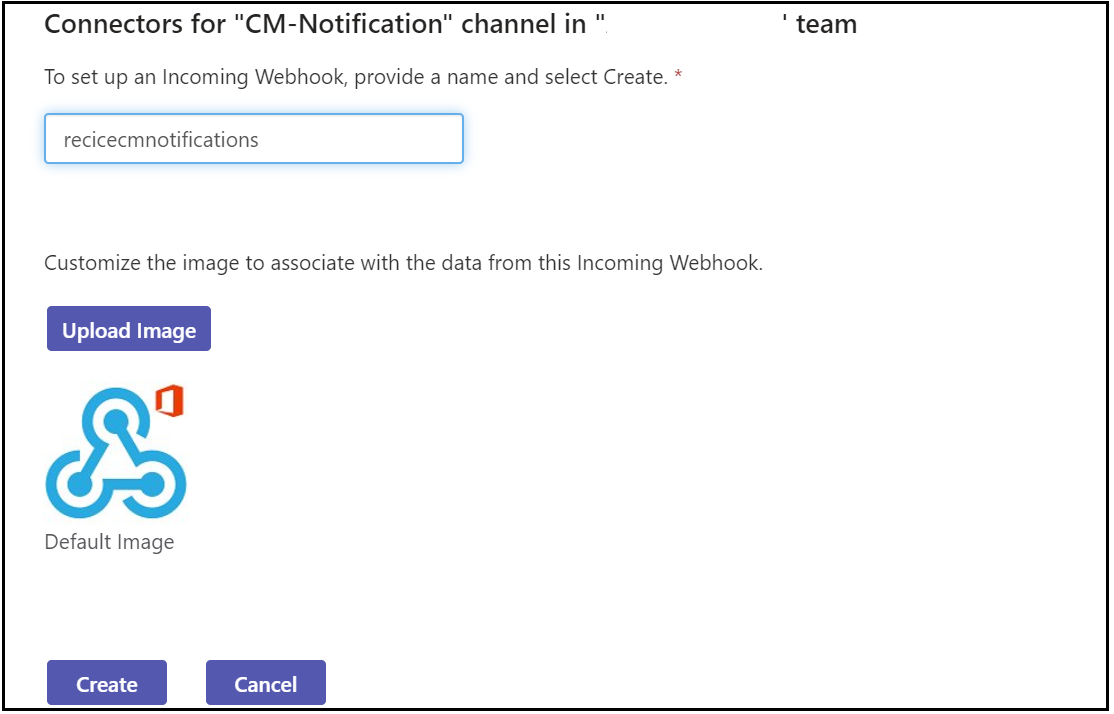
Enter a name and click on create, if required upload a custom image to display on incoming messages.
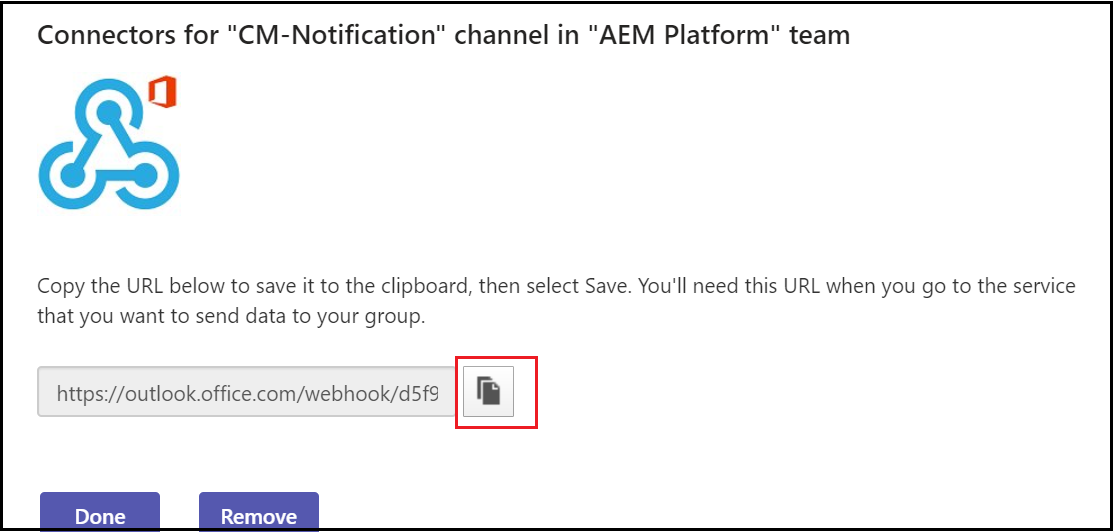
Copy the webhook URL and click on Done
Enable Adobe I/O Configurations:
Let us enable the required configurations in Adobe I/O, log in to console.adobe.io
Create a new project, edit the project and provide a custom name if required
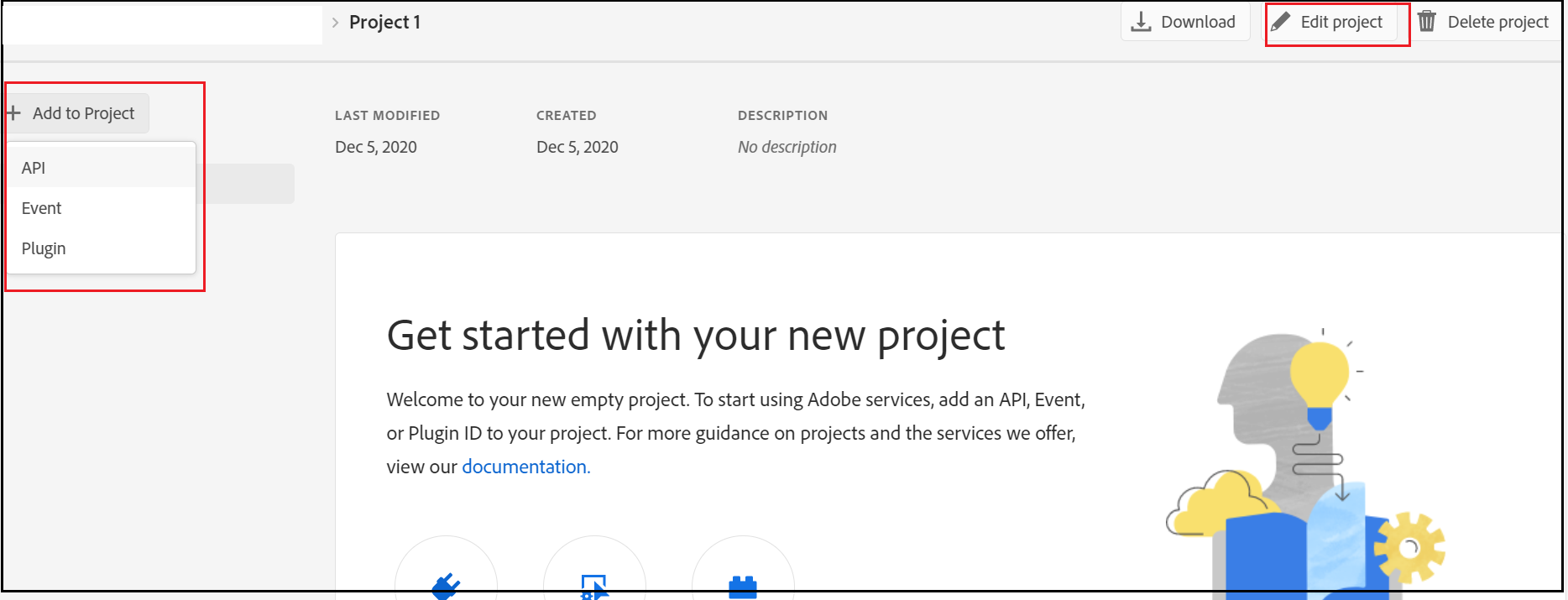
Add Cloud Manager API to the Project
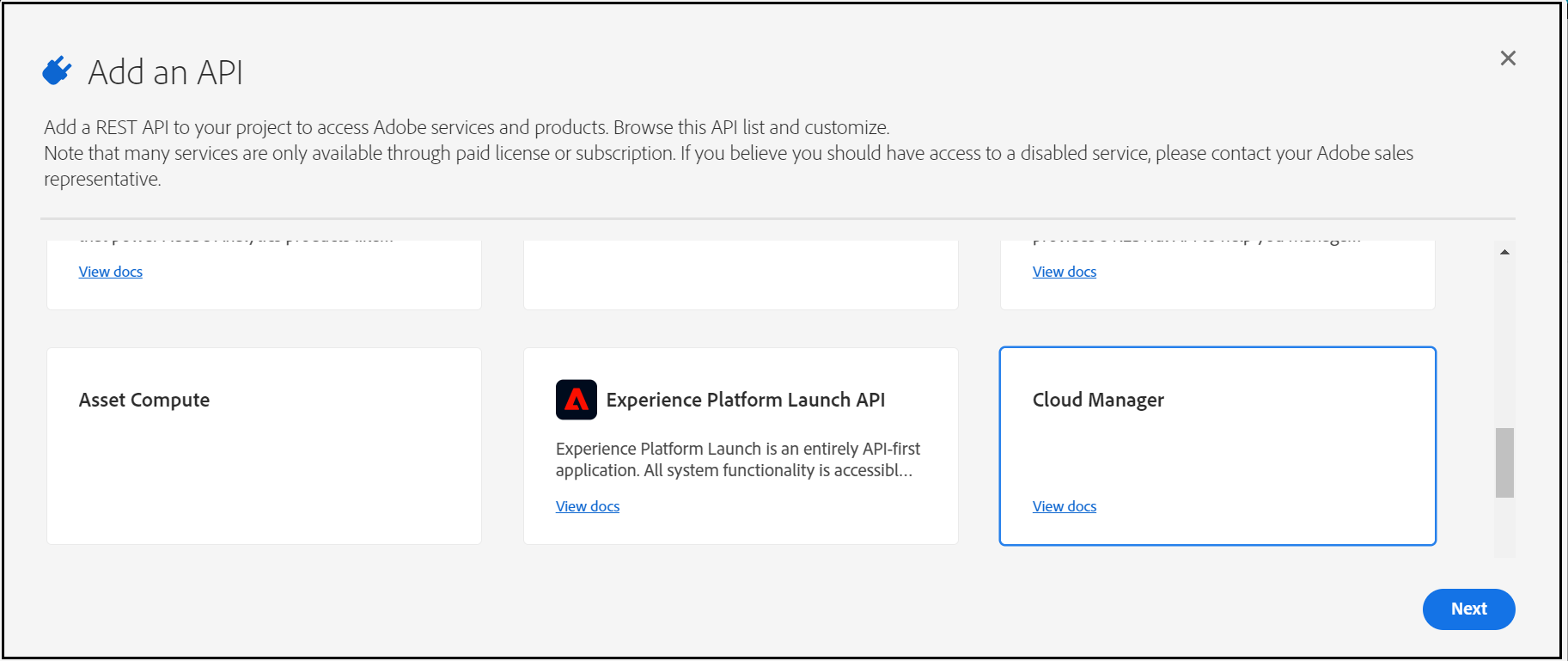
Now “Generate a key pair”
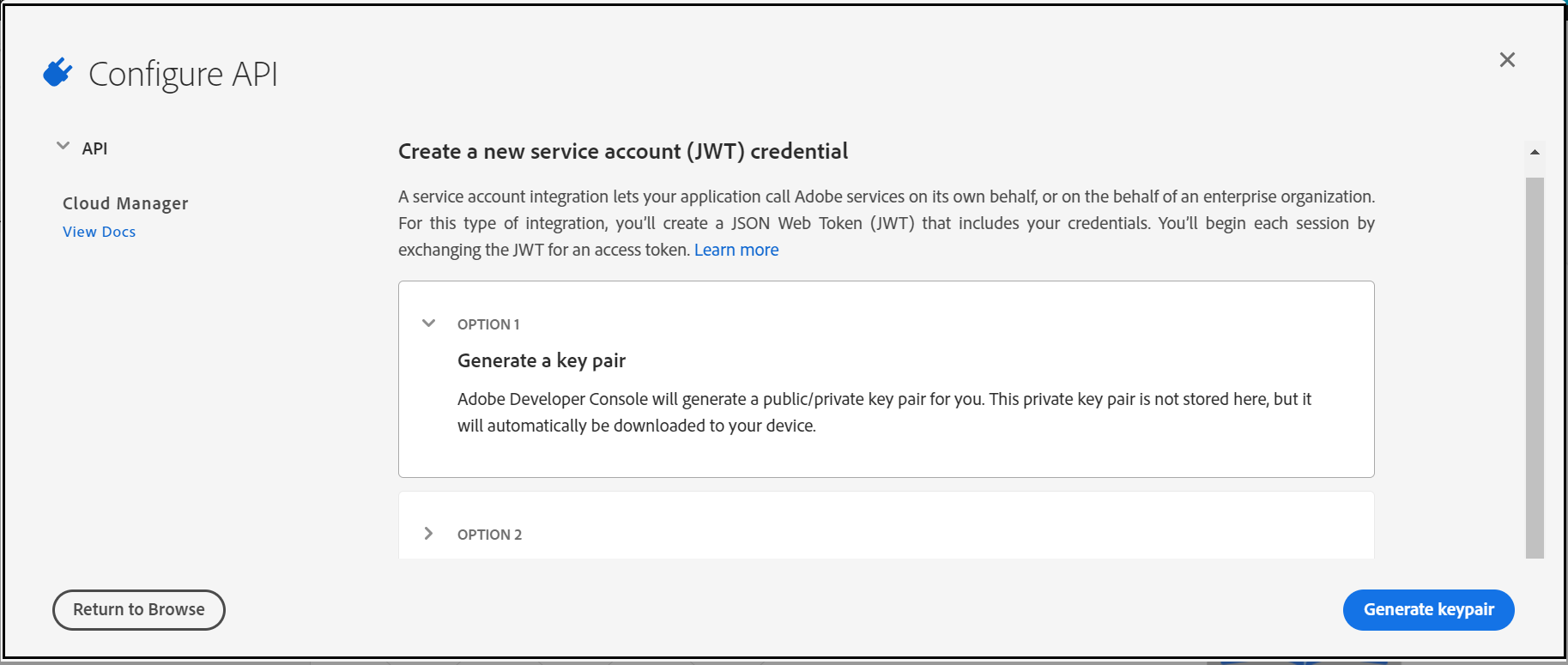
This will download a “config.zip” with a public certificate and private key(need to be configured in the AEM Service)
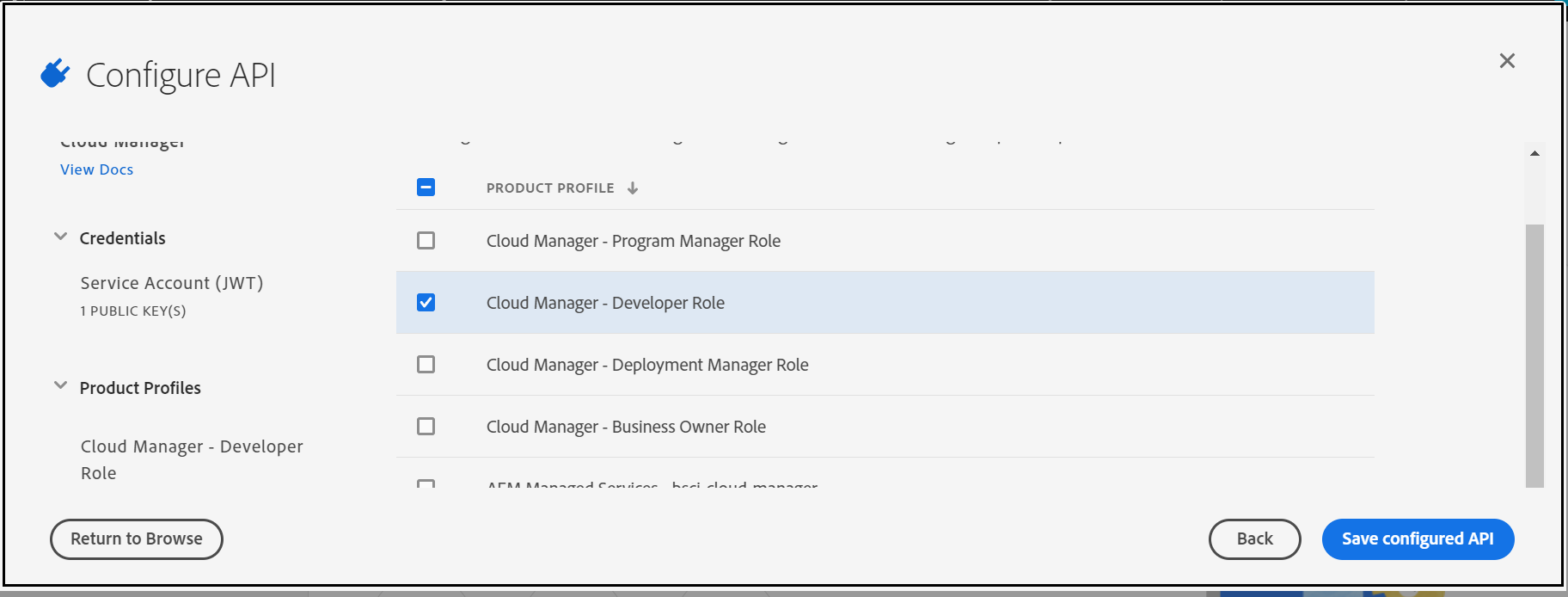
Assign the Cloud manager role to enable the required permissions to the API — “Cloud Manager-Developer Role” should be enough to perform the API operations.
Add Cloud Manager Events to the project
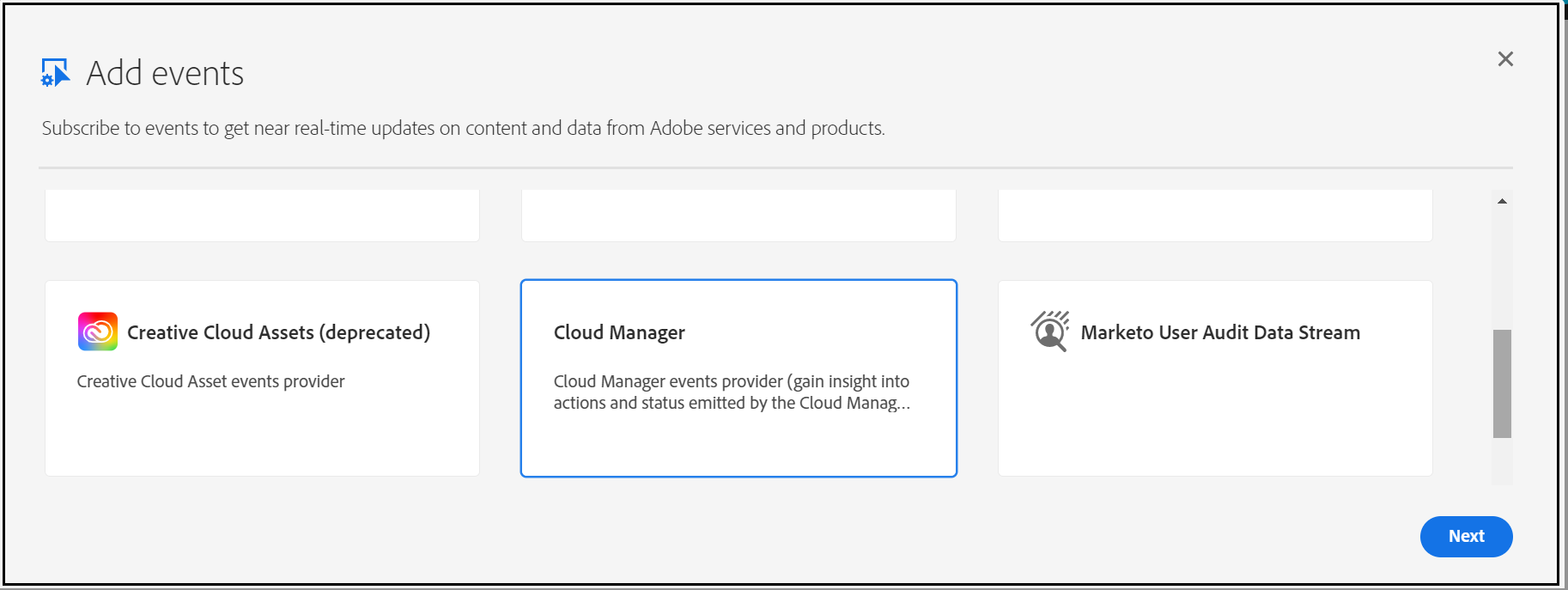
Subscribe to the required Events — I am subscribing only for “Pipeline Execution Started”, current AEM service is enabled to handle only this start event.
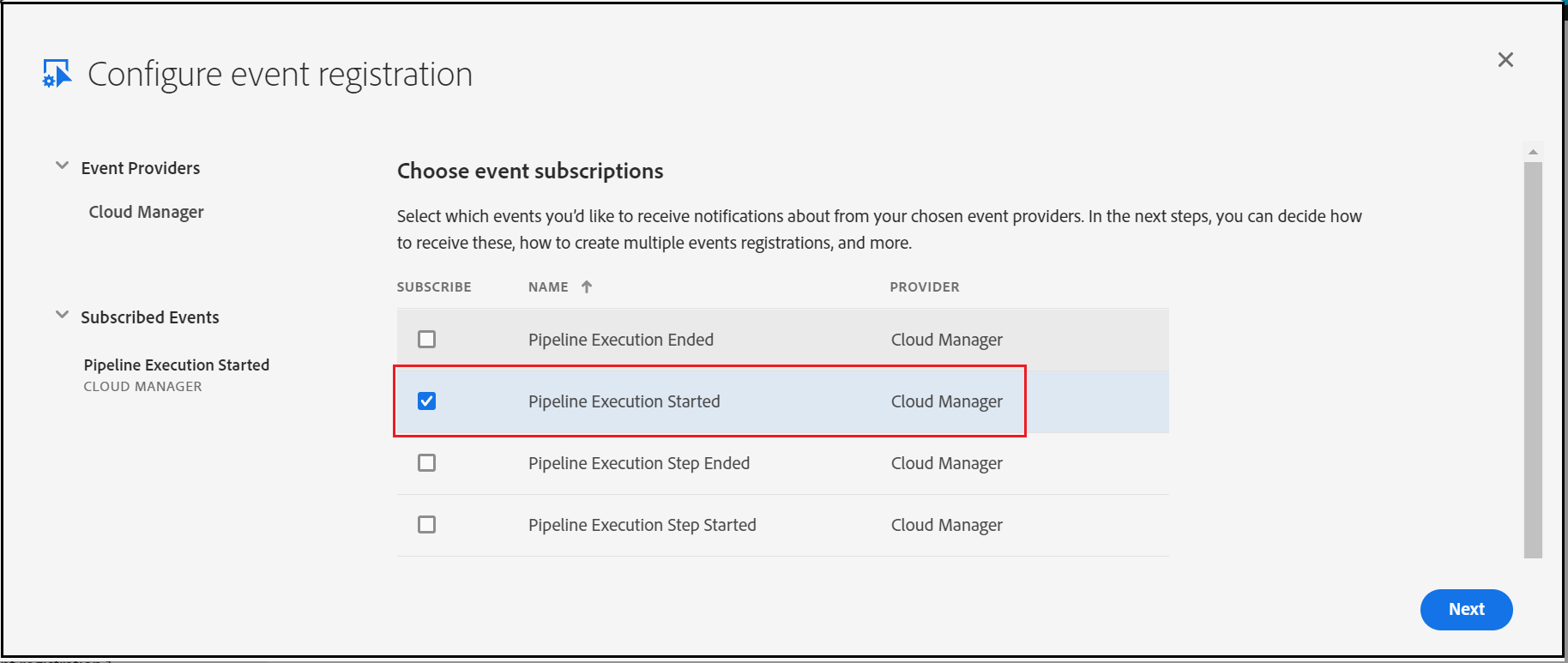
Enter the AEM service URL (/bin/cmnotification) — I am using ngrok to expose AEM URL externally for demo(use AEM external service URL)
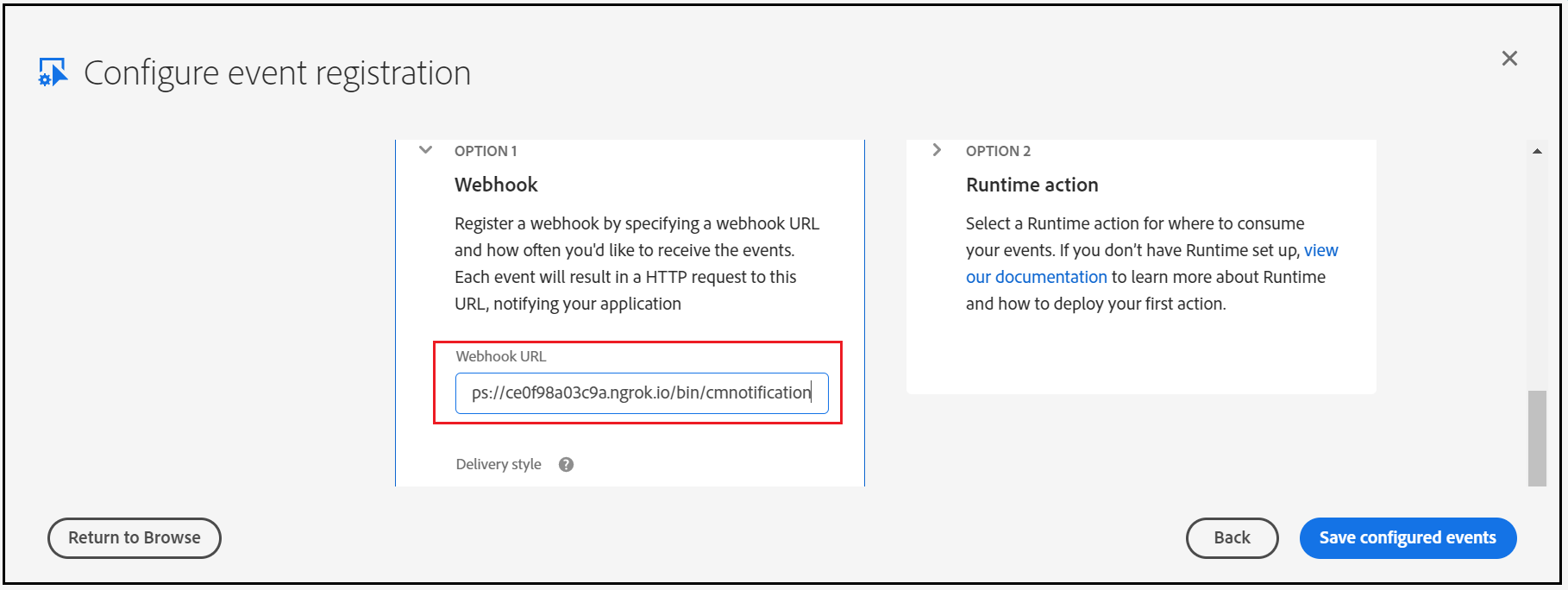
Now the Adobe I/O configuration is ready, let us enable the service in AEM.
Enable Custom Webhook in AEM:
I am enabling the below servlet to accept the requests from Adobe I/O
- GET Service to support challenge service
- POST service to accept the Event details
Post Service:
- Validate the Signature of the incoming request
- Parse the Event Data
- Generate signed(private key) JWT bearer token
- Request for Accesses token with the JWT bearer token
- Invoke API to receive the execution details based on the execution URL in the Event Data
- Invoke the API to receive the pipeline details based on the pipeline URL in the Execution details(different URL's from the execution details can be used to fetch different data)
- Notify teams channel with Teams Channel Webhook
Configure the below values into the servlet(the values can be modified through the OSGI console)
The required values can be retrieved from the Adobe I/O console
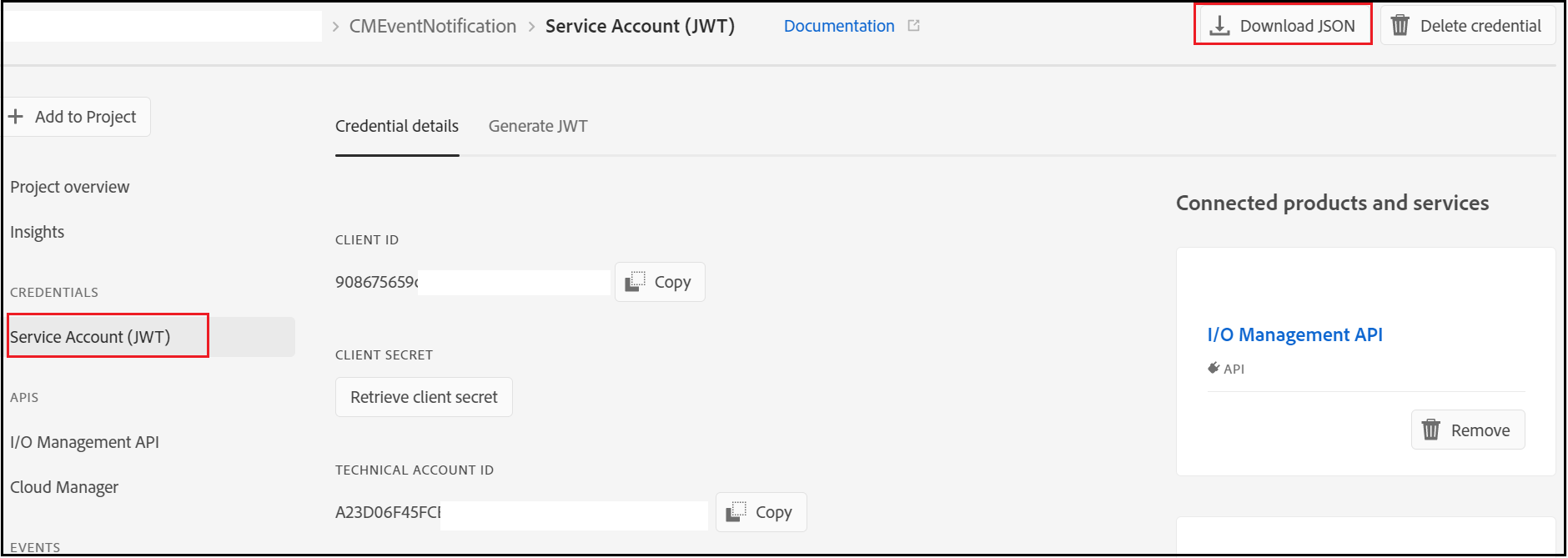
TECHNICAL_ACCOUNT_EMAIL
TECHNICAL_ACCOUNT_ID
API_KEY(CLIENT_ID)
CLIENT_SECRET
TEAMS_WEBHOOK — The Webhook URL enabled in Teams
The AEM bundle can be downloaded from here https://github.com/techforum-repo/bundles/tree/master/CMNotificationHandler
Copy the private.key file(from the config.zip file downloaded earlier) to the bundle under /META-INF/resources/keys.
Deploy the bundle to the AEM server (mvn clean install -PautoInstallBundle -Daem.port=4503)
Now the webhook service is ready
Initiate a pipeline from Cloud Manager Portal that will trigger the notification to the Teams Channel.
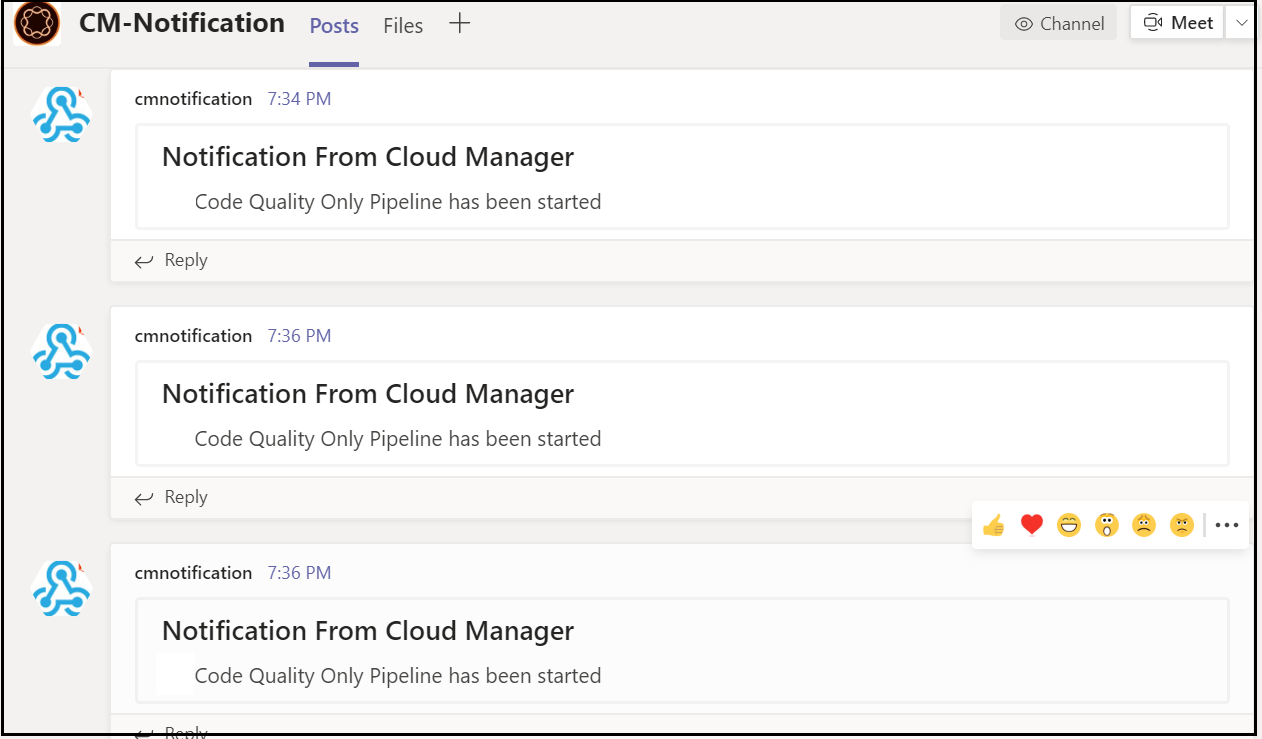
Currently, the notification will be sent only when the pipeline is started, extend the bundle to support different events and to fetch the additional details from different endpoints — the URL’s can be taken from the JSON response of the parent APIs. This will helps us to receive the notification into the team's channel on pipeline events. This approach may add some additional overhead to the AEM server but not required to maintain any additional platforms, Adobe I/O approach needs the license to the Adobe I/O platform.
Feel free to provide your comments.
Friday, December 4, 2020
init failed:Error: not supported argument while generating JWT token with jsrsasign - Node JS
I was getting "init failed:Error: not supported argument" error while trying to generate the JWT Token with RS256 algorithm through "jsrsasign" npm module.
const jsrsasign = require('jsrsasign')
const fs = require('fs');
const EXPIRATION = 60 * 60 // 1 hour
const header = {
'alg': 'RS256',
'typ': 'JWT'
}
const payload = {
'exp': Math.round(new Date().getTime() / 1000) + EXPIRATION,
'iss': 'test',
'sub': 'test',
'aud': 'test',
'custom-prop': 'test'
}
const privateKey = fs.readFileSync('privateKeyfile.key);
const jwtToken = jsrsasign.jws.JWS.sign('RS256', JSON.stringify(header), JSON.stringify(payload), JSON.stringify(privateKey))
But the JWT token generation was successful with the HS256 algorithm
const jsrsasign = require('jsrsasign')
const fs = require('fs');
const EXPIRATION = 60 * 60 // 1 hour
const header = {
'alg': 'HS256',
'typ': 'JWT'
}
const payload = {
'exp': Math.round(new Date().getTime() / 1000) + EXPIRATION,
'iss': 'test',
'sub': 'test',
'aud': 'test',
'custom-prop': 'test'
}
const privateKey = fs.readFileSync('privateKeyfile.key);
const jwtToken = jsrsasign.jws.JWS.sign('HS256', JSON.stringify(header), JSON.stringify(payload), JSON.stringify(privateKey))
To support the RS256 algorithm, changed the "jsrsasign" to "jsonwebtoken" module.
const jwt = require('jsonwebtoken');
const fs = require('fs');
const EXPIRATION = 60 * 60 // 1 hour
const header = {
'alg': 'HS256',
'typ': 'JWT'
}
const payload = {
'exp': Math.round(new Date().getTime() / 1000) + EXPIRATION,
'iss': 'test',
'sub': 'test',
'aud': 'test',
'custom_attr': 'test'
}
const privateKey = fs.readFileSync(process.env.PRIVATE_KEY);
const jwtToken=jwt.sign(JSON.stringify(payload), privateKey,{ 'algorithm': 'RS256' });
The JWT token generation with the RS256 algorithm was successful after switching to "jsonwebtoken" module
Sunday, November 29, 2020
How to Register Servlets Dynamically in AEM?
Most of the time while working on the project we will have scenarios to dynamically register the servlets with different resource types, selector and extension, etc — registering the same servlet with different resource types, selector, extensions, etc.
Let's assume we have a servlet that is registered with a specific resource type but later we have a requirement to enable the same servlet for a different resource type, one of the common options is modifying the source code to enable the additional resource types. The code change might not be the optimal solution in most cases.
In this tutorial, let us see the simple approach to register the servlets dynamically with different resource types, selectors, and extensions.
The OSGi Metatype Annotations(OSGi Declarative Services Annotations) can be used to register the dynamic servlets.
ObjectClassDefinition — Generate a Meta Type Resource using the annotated type
AttributeDefinition — AttributeDefinition information for the annotated method.
Designate — Generate a Designate element in the Meta Type Resource for an ObjectClassDefinition using the annotated Declarative Services component.
I am creating a servlet with the name DynamicResourceTypeServlet, Created a @ObjectClassDefinition inside the servlet with required AttributeDefinitons with servlet registration
Define a Designate to the servlet to the ObjectClassDefinition.
Deploy the bundle and configure the required resource types, selector, and extensions from ConfigMgr(http://localhost:4503/system/console/configMgr/com.sample.servlets.DynamicResourceTypeServlet)
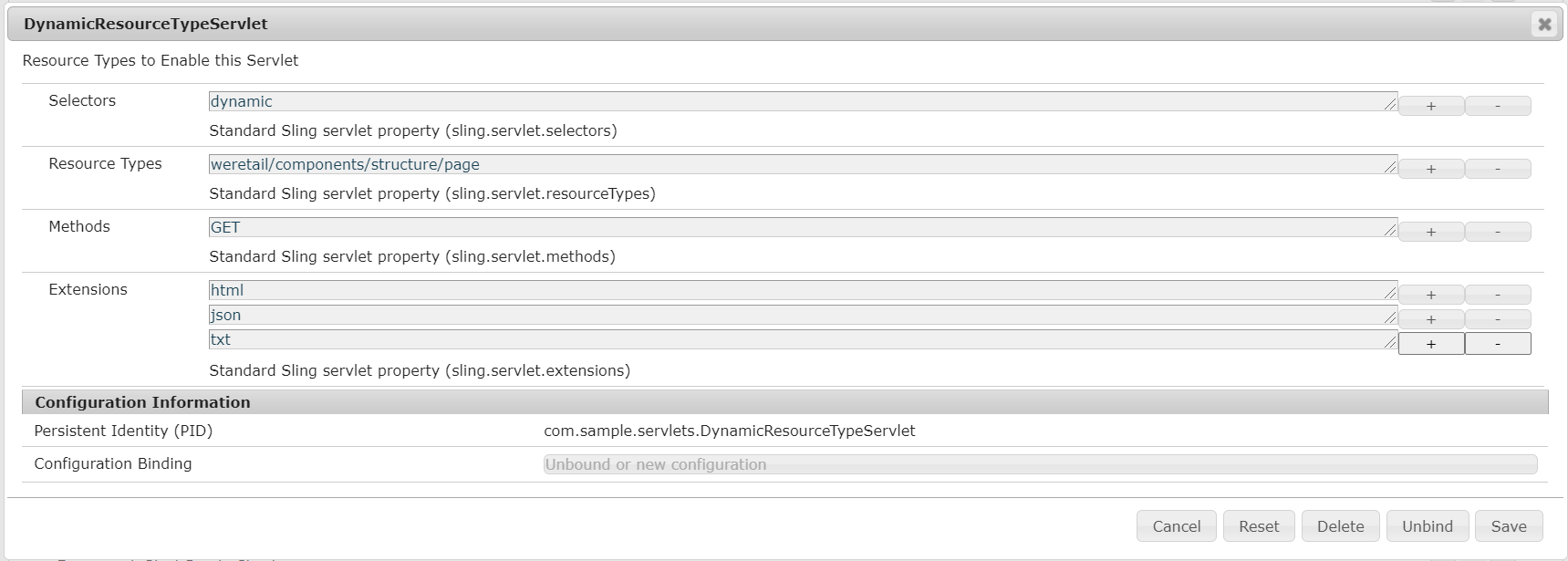
Now the servlet is registered with configured resource types, selectors, and extensions.
The servlet can be accessed through the below URL’s (the resource type for /content/wknd/us/en is wknd/components/page)
Add the below dependency into the core module to enable the DS annotations
<groupId>org.osgi</groupId>
<artifactId>org.osgi.service.metatype.annotations</artifactId>
<version>1.4.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
The bnd-maven-plugin generate the required OSGi meta-type definitions for the annotations during compile time. The dynamic servlet registration is a useful feature that helps to register the servlets dynamically with different resource types, selectors, and extensions.
Feel free to provide your comments.
Monday, November 23, 2020
Beginners Tutorial: What is Cloud Manager for Adobe Experience Manager(AEM)?
What is Cloud Manager for AEM?
- Cloud Manager is a Cloud service that allows customers to build, test, and deploy AEM applications hosted by Adobe Managed Services.
- Enables customers to manage their custom code deployments on their AEM-managed cloud environments with manageable pipeline automation and complete flexibility for their deployment timing or frequency.
- Each customer gets its own Git Repository and their code is secure and not shared with any other Organizations.
- Cloud Manager is only available to Adobe Managed Services customers using AEM 6.4 or above
- Restructure the code with the latest arch type to support the Dispatcher deployment
- Address the quality issues and adhere to the best practices for onboarding into Cloud Manager
- Define application-specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Key Features
Self Service interface:
- Enables customers to easily access and manage the cloud environment and CI/CD pipeline for their Experience Manager applications.
- Helps to define application-specific KPI's like peak page views per minute and expected response time for a page load,
- Helps to define Roles and permissions for different team members.
CI/CD pipeline:
- Setup optimized CI/CD pipeline to speed the delivery of custom code or updates such as adding new components on the website.
- Allows AEM project teams to quickly, safely, and consistently deploy code to all AEM environments hosted in AMS
- A thorough code scan is executed to ensure that only high-quality applications pass through to the production environment.
- Quality checks include, code inspection, security testing, and performance testing are always performed as part of the CI/CD pipeline execution
Flexible Deployment Modes:
- Cloud Manager offers customers flexible and configurable deployment modes so they can deliver experiences according to changing business demands
- In automatic trigger mode, the code is automatically deployed to an environment based on specific events such as code commit.
- You can also schedule code deployments during specified time frames, even outside business hours.
- Manual – trigger the deployment manually
Auto Scaling:
The autoscaling feature will apply only to the Dispatcher/Publish tier, and will always be executed using a horizontal scaling method, with a minimum of one additional segment of a Dispatcher/Publish pair, and up to a maximum of ten segments.
Cloud Manager Benefits:
- Enables organizations to self-manage Experience Manager in the cloud
- Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery of code to reduce time to market from months/weeks to days/hours
- Cloud Manager provides continuous delivery and continuous integration for updates with zero downtime.
- Code Inspection, performance testing, and security validation based on best practices before pushing to production to minimize production disruptions.
- Automatic, scheduled or manual deployment even outside of business hours for maximum flexibility and control.
- Autoscaling feature intelligently detects the need for increased capacity and automatically brings online additional Dispatcher/Publish segment(s).
- Reduce the dependency with Adobe CSE for production deployment
- Configure a set of content paths which will either be invalidated or flushed from the AEM Dispatcher cache for publish instances
- Development on your local git repositories ate integrate with CM Git repository
- API/Events/Webhooks for external tool integration through Adobe I/O
CI/CD Pipeline:
- Non-Prod Pipeline
- Production Pipeline
- Code Quality Pipeline
- Deployment Pipeline
Non-Prod - Code Quality Pipeline
- Code Quality pipelines execute a series of steps on a code from a Git branch to build and be evaluated against Cloud Manager’s code quality scan
- Helps to identify and fix the quality issues before planning for production deployment.
- Code quality pipeline can be used before provisioning the environments
- Quality report for review
Non-Prod - Deployment Pipeline
Production Pipeline
- manually,
- with a Git commit
- based on a recurring schedule
- Application for Approval (if enabled)
- Schedule Production Deployment (if enabled)
- CSE Support (if enabled)
Cloud Manager Quality:
Code quality testing:
Security testing:
Performance testing:
Cloud Manager Roles
Cloud Manager API
- The Cloud Manager API enables Cloud Manager customers to interact with the same underlying capabilities exposed through the web UI in a fully programmatic fashion
- This allows for the integration of the Cloud Manager Continuous Integration / Continuous Delivery pipeline with other systems.
- The API’s are managed through Adobe I/O
- By using Adobe I/O Events, Cloud Manager can send external applications notifications when key events occur
- Starting the Cloud Manager CI/CD pipeline from an external system.
- Executing additional tests between the standard Cloud Manager performance tests and the ultimate production deployment.
- Triggering additional activities after the pipeline execution is complete or a specific step has been completed, for example
- CDN cache invalidation once the production deployment is finished.
- Deploying related applications to non-managed Services systems.
- Notifying on other channels (e.g. Slack, Microsoft Teams).
- Creating issue reports in bug tracking systems (e.g. Atlassian JIRA) on pipeline failures