Content personalization in short means delivering the right content to the right person in real-time.

Simple experience targeting scenario, user1 requesting the content through Firefox receives Experience A and user2 requesting the content through Chrome receives Experience B. The experience can be decided based on different rules e.g gender, age location, etc, here we are seeing the simple scenario.
The targeting engine is the mechanism that drives the logic for targeted content. You can use either AEM or Adobe Target as the targeting engine, AEM provides a built-in targeting engine that processes page requests and determines the content to display. AEM as a targeting engine only supports Experience Targeting but Adobe Target should be used for A/B testing.
In this post, let us see how to use the AEM targeting engine to enable the experience targeting for a web page.
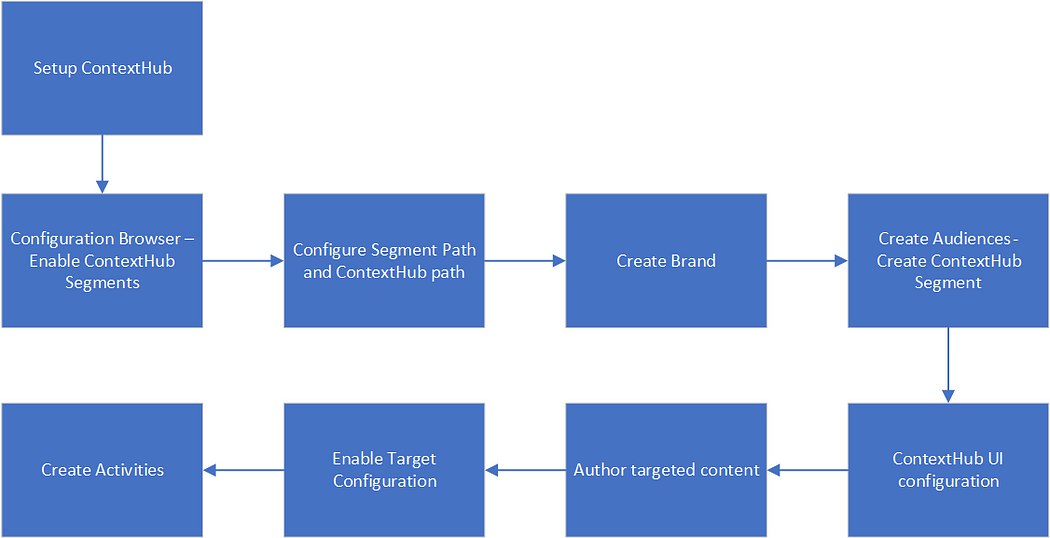
Setup ContextHub:
ContextHub is a framework for storing, manipulating, and presenting context data. The ContextHub Javascript API enables you to access stores to create, update, and delete data as necessary. To enable the ContextHub features and to link to the ContextHub JavaScript libraries, including the <contexthub> component in the <head> section of your web page.
Add the below HTL code to the overridden customheaderlibs.html file of your page component(here the page component is extending from core page component — core/wcm/components/page/v2/page
<sly data-sly-resource="${'contexthub' @ resourceType='granite/contexthub/components/contexthub'}"/>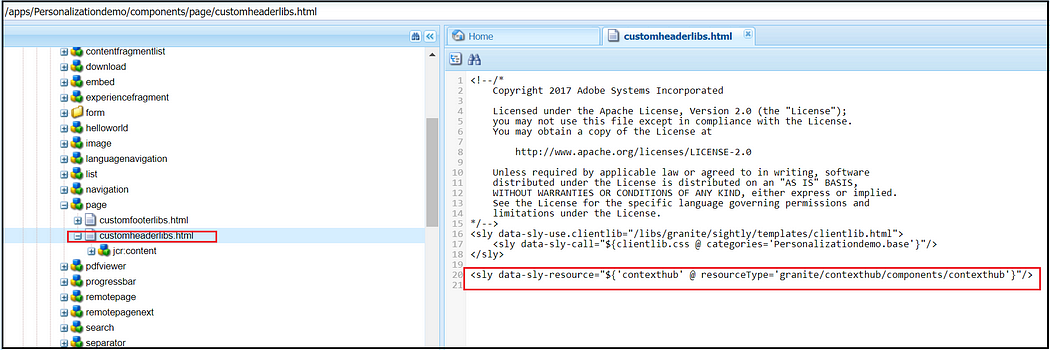
ContextHub includes a segmentation engine that manages segments and determines which segments are resolved for the current context.
Once the ContextHub is enabled for the project client context data can be explored through the browser local storage.
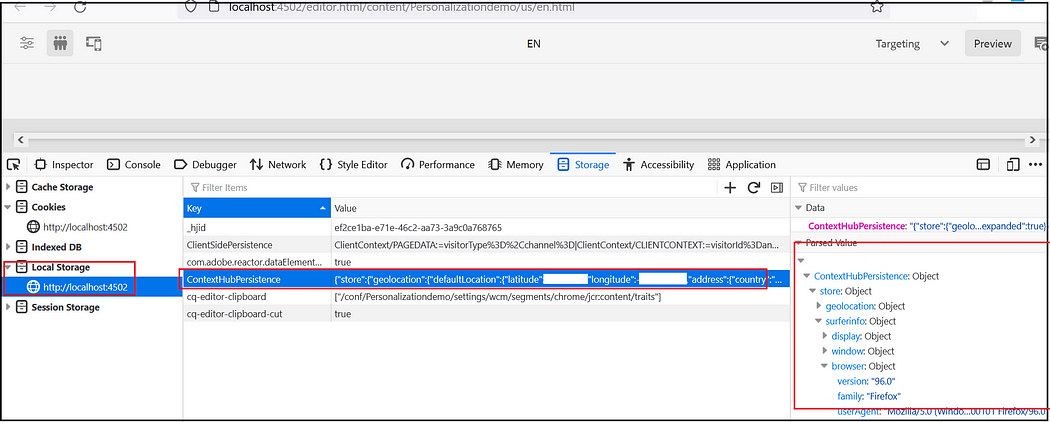
Refer to https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/experience-manager-65/developing/personlization/contexthub.html for more details on ContextHub.
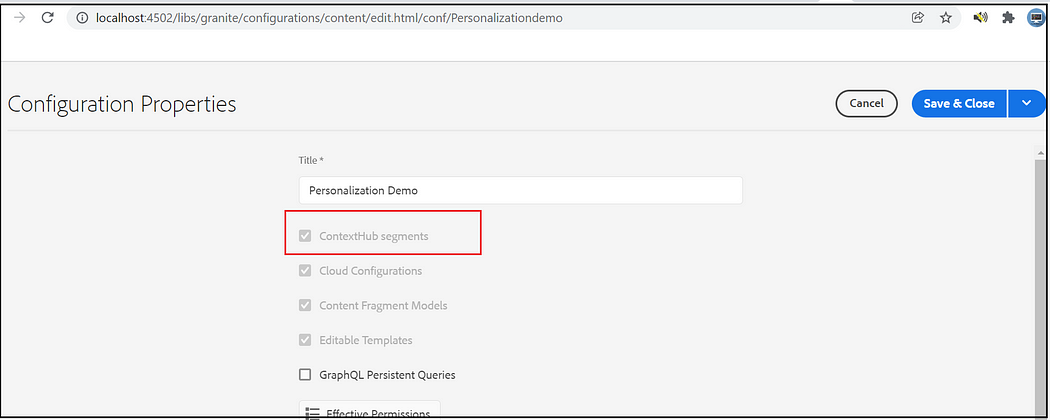
Configuration Browser — Enable ContextHub Segments:
Enable the ContextHub segments for your site under Configuration Browser. Tools → General → Configuration Browser → Select the project → Properties → Select ContextHub Segments, Save and Close
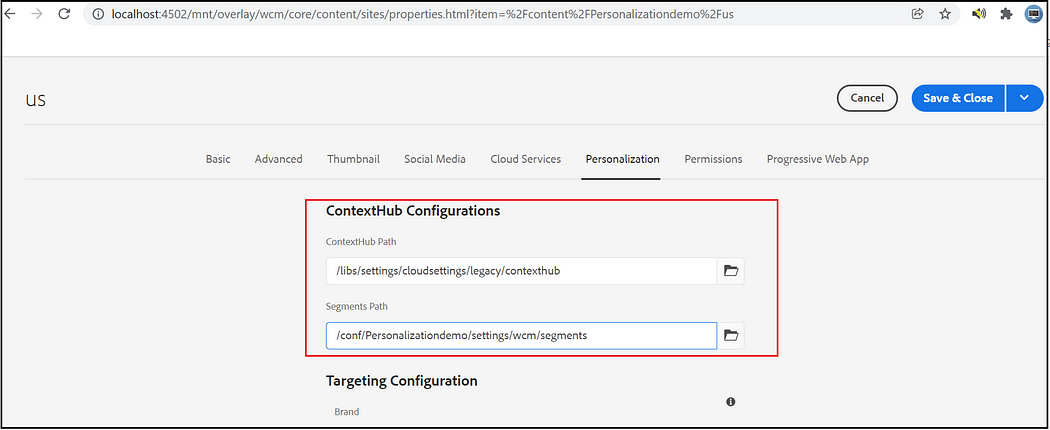
Configure Segment Path and ContextHub path:
Assign Segment path and ContextHub path to your site root node, the default ContextHub path is /libs/settings/cloudsettings/legacy, segment path — /conf/<tenant>/settings/wcm/segments
Create Brand:
Create a Brand to manage the Audiences through Activities console, Tools →Personalization →Activities, Create Brand
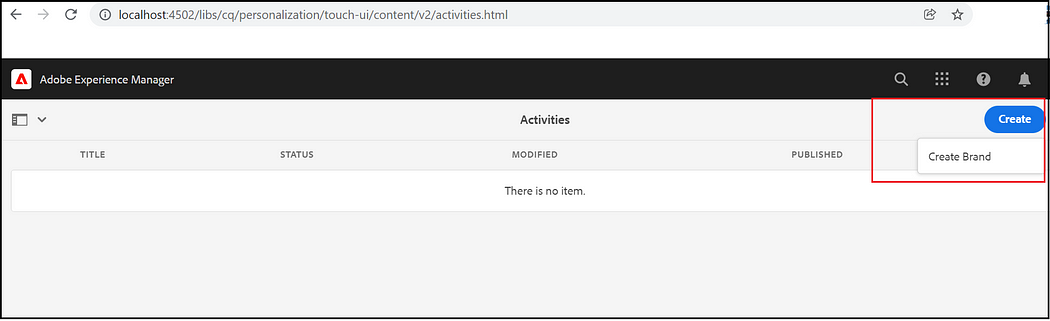
Select Brand Template, add a tile, and Create
Create Audiences — Create ContextHub Segment:
An audience, called segment in ContextHub, is a class of visitors defined by specific criteria, which then determines who sees a targeted activity.
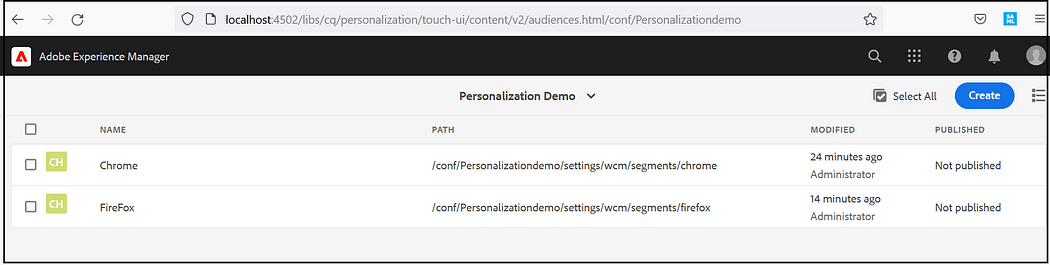
Create the required Audiences, Tools →Personalization →Audiences, Create ContextHub Segments under the corresponding project.
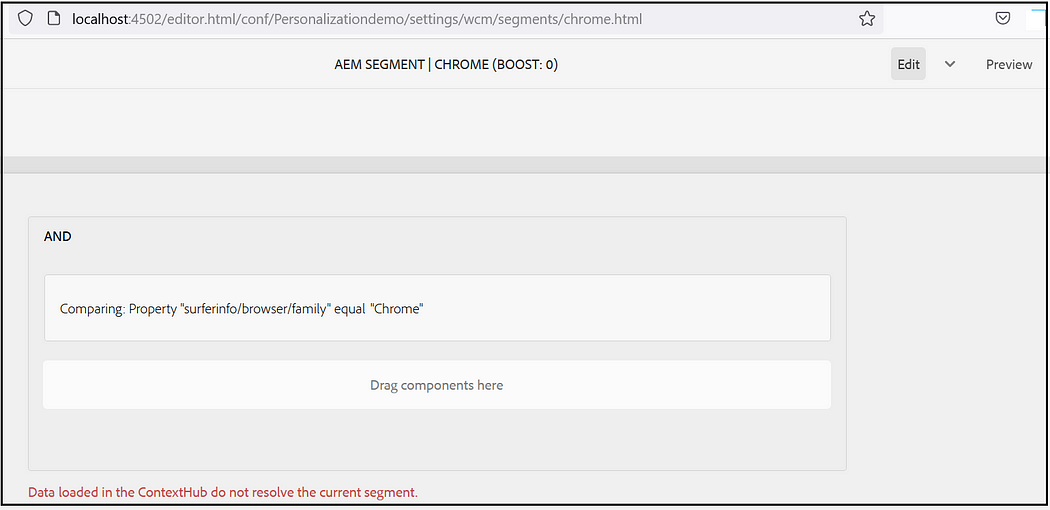
I am creating two Audiences, one for Chrome browsers and another one for Firefox with the simple conditions to check the browser from which the request coming. Specify the required boost factor, If there is more than one segment that gets resolved the one with a higher boost factor is selected.
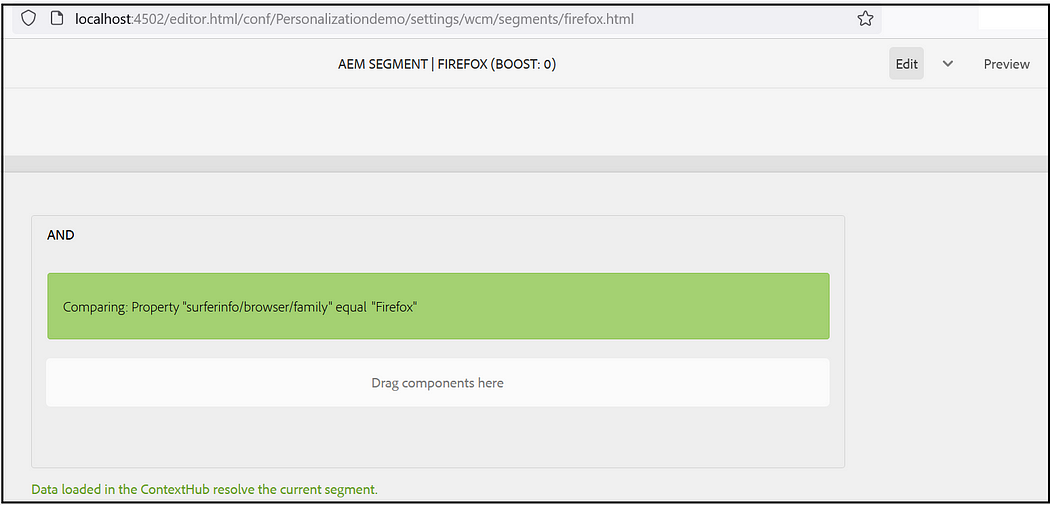
Assign the segments to the audience, I am using “CONTEXTHUB SEGMENTATION: Comparision: Property — Value” with the simple conditions to check the browser name(complex rules can be enabled based on the use cases)
Create Activities:
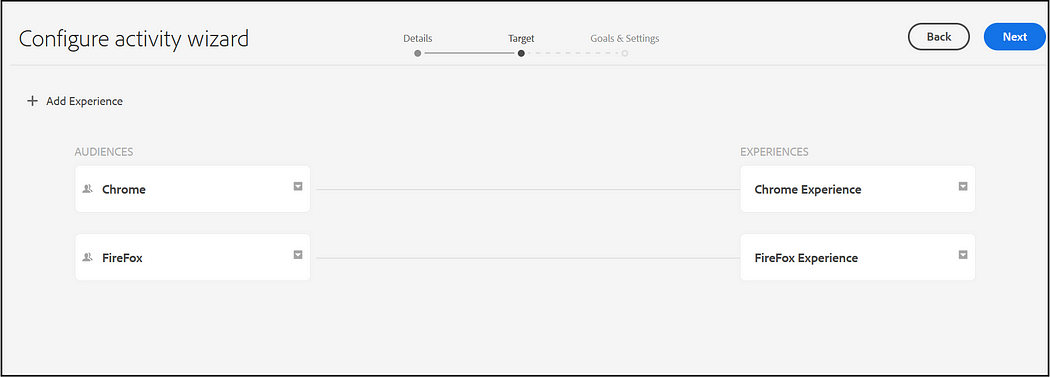
Activities consist of audiences that you are targeting, and the period of time when the targeting is applied.
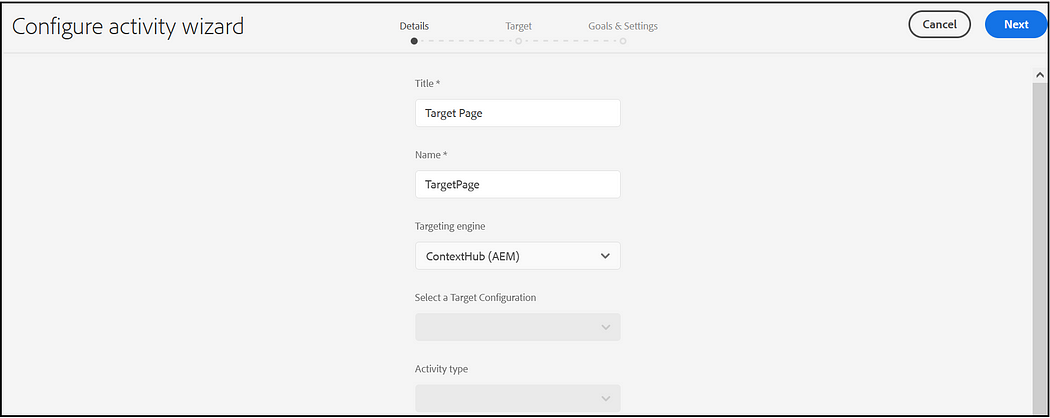
First Create an Area under Brand and create the Activity inside the Area, Tools →Personalization →Activities
Enter Title, Name and select the Target Engine as ContextHub
Add Experience for each audience
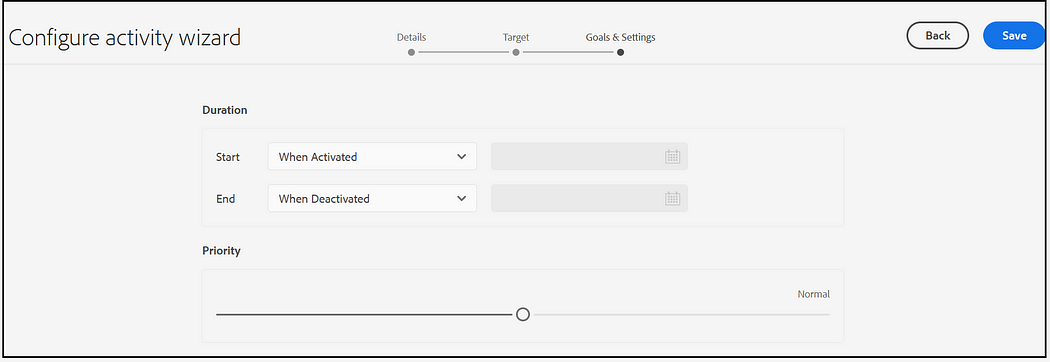
Set the Duration and Priority
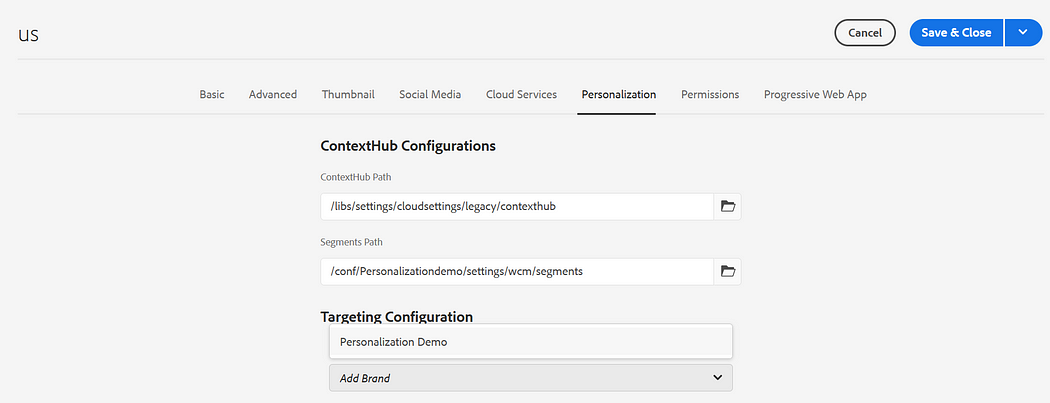
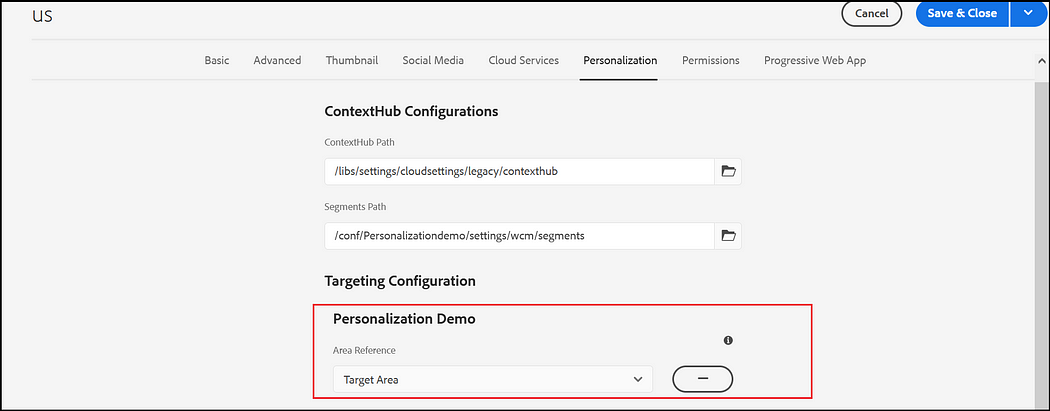
Enable Target Configuration:
Enable the Target Configuration — Brand, Area to the root page properties or to the specific page(you can configure more than one brand).
Author targeted content:
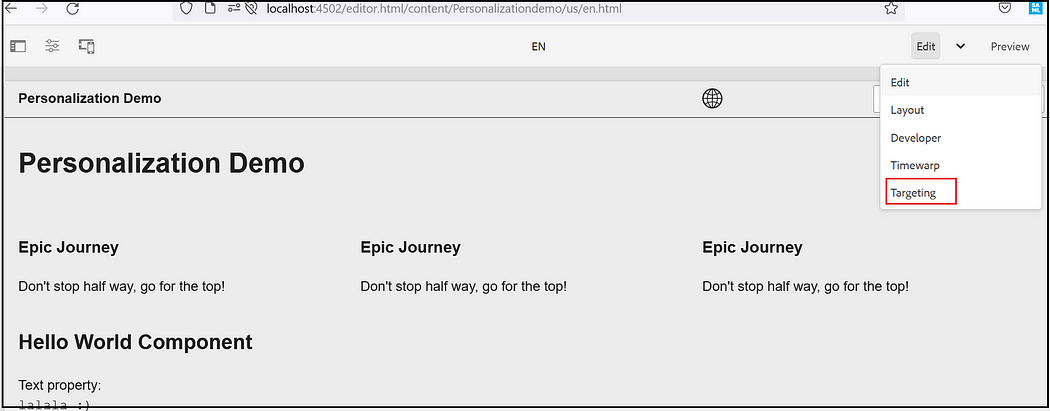
Author targeted content using the Targeting mode of AEM. Targeting mode provides tools for creating content for the experiences of your marketing activities.
Select Targeting Mode from the Dropdown
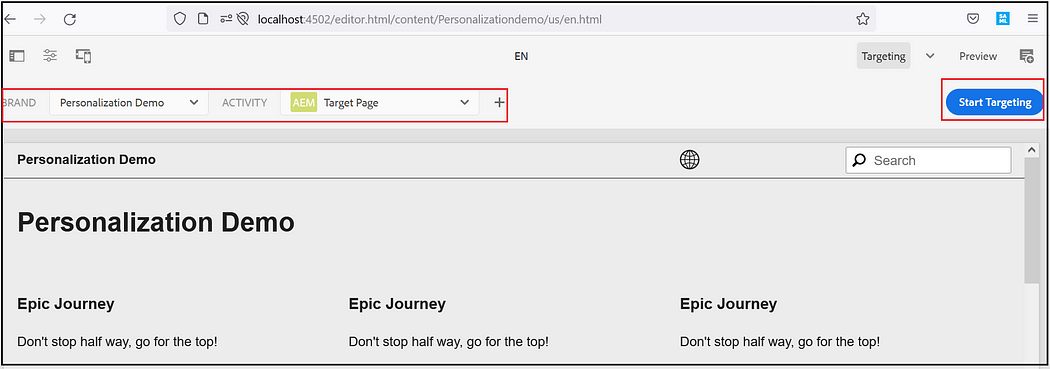
Select the Brand and Activity and click on Start Targeting.
On required components select the Target option
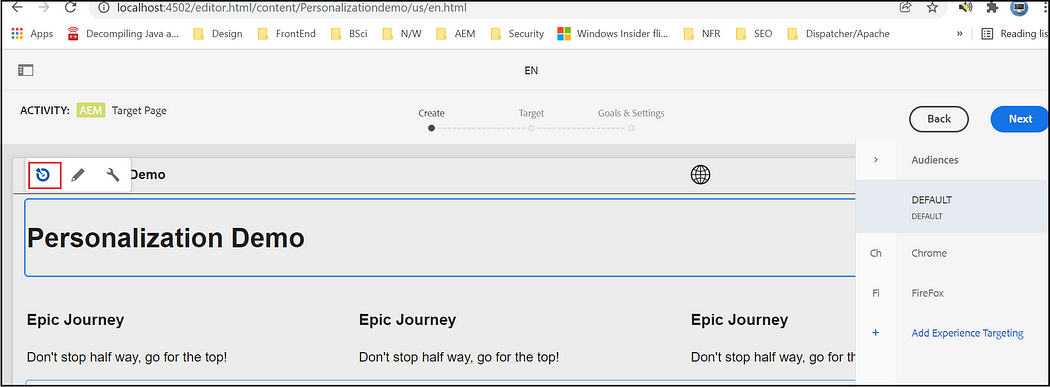
Now select the Audience and define the experience for the components, Default — Default experience, Chrome — the experience for the Chrome user, Firefox — the experience for the Firefox user. Select the corresponding audience and edit the component data.
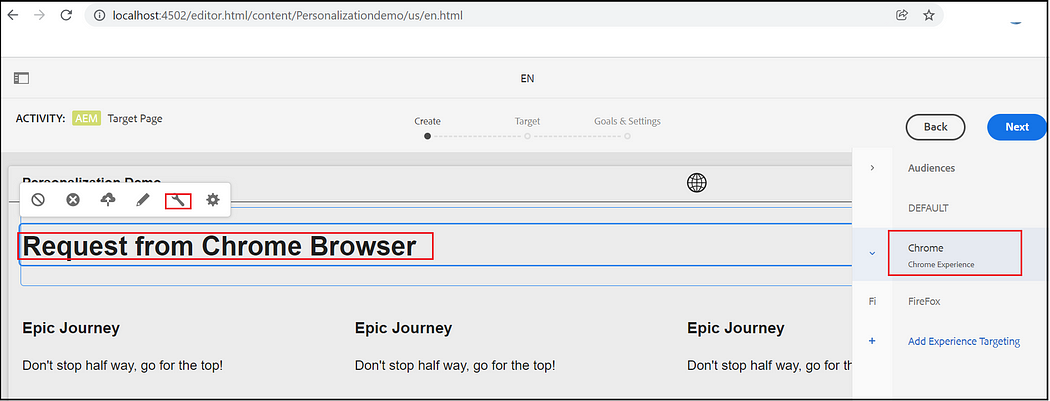
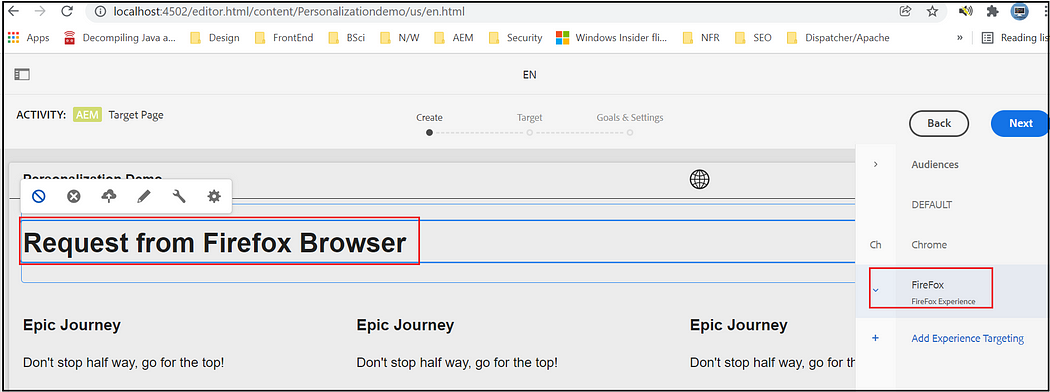
Now you will get different experiences while accessing the page from Firefox and Chrome browsers.
Chrome -
Firefox —
IE — Default behavior
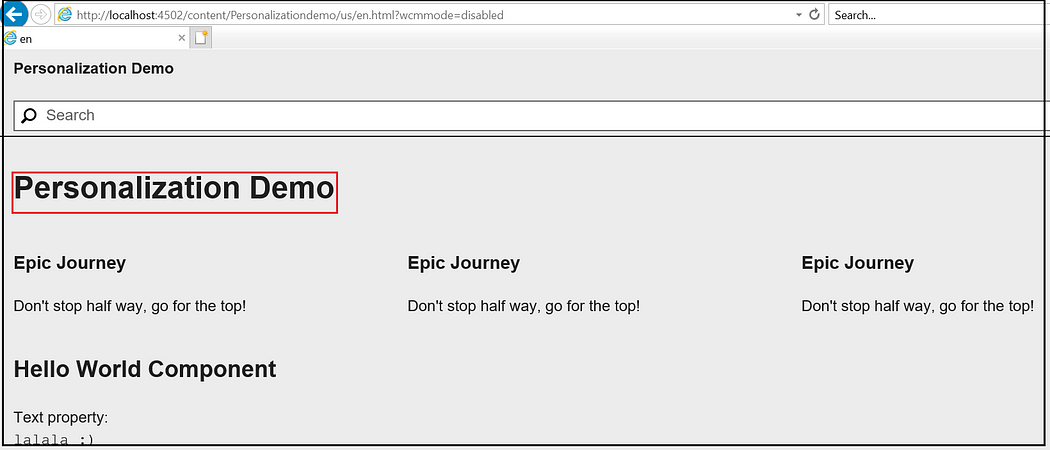
ContextHub UI configuration:
ContextHub provides a toolbar for content authors to allow display and manipulation of client context data in order to achieve a reliable preview of experience targeting. The toolbar is fully customizable and configurable.
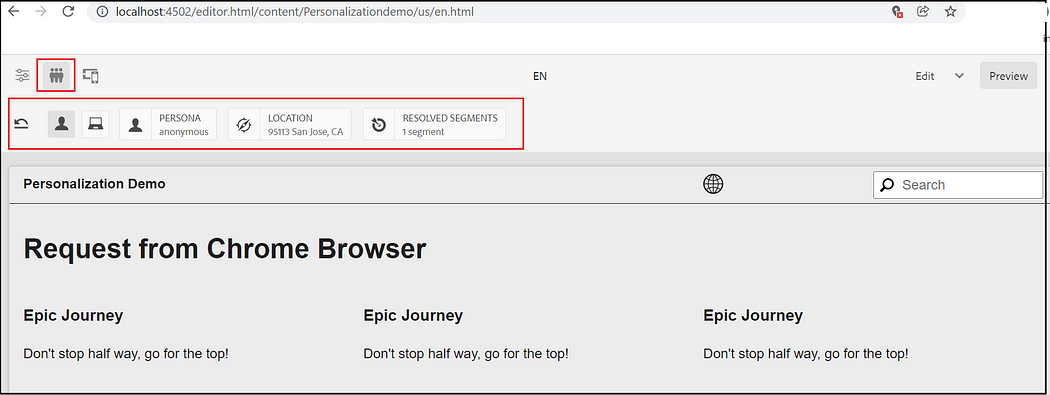
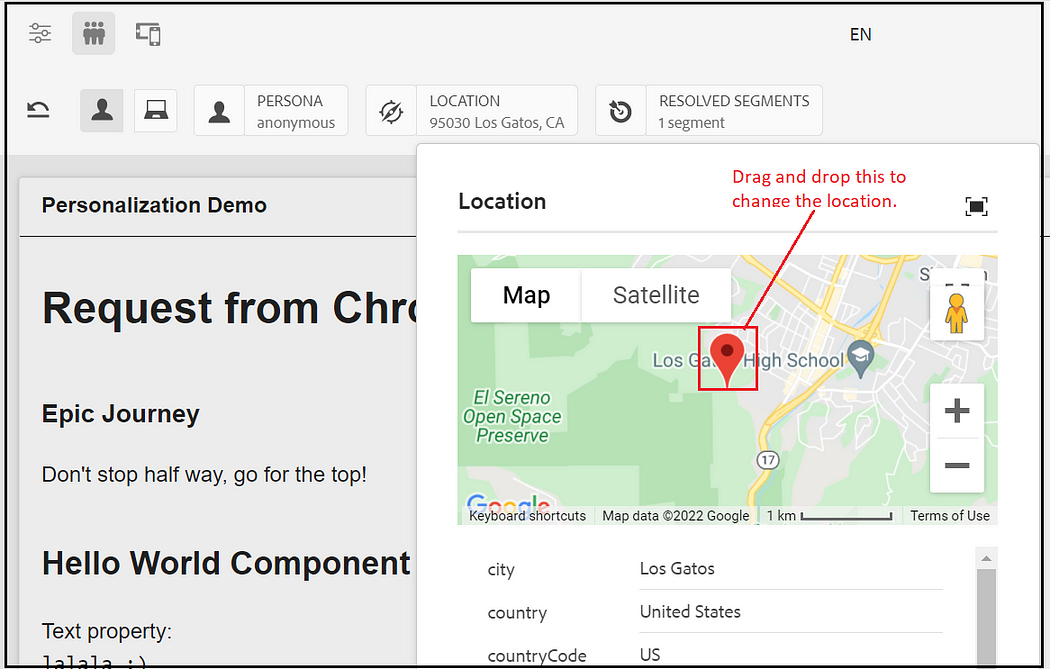
The location can be changed to preview different experiences.
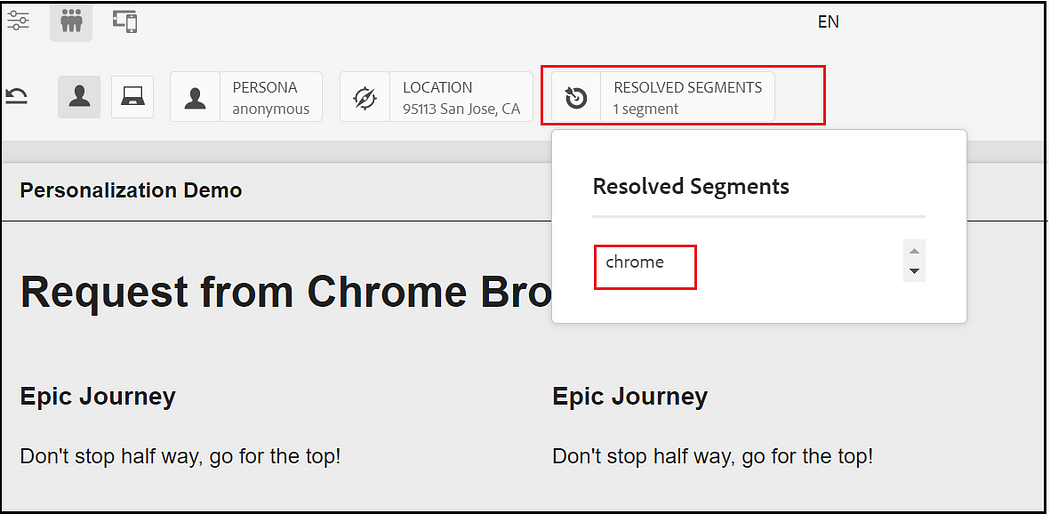
Also, you can find the resolved segments
The resolved segment details can also be referenced from browser local storage
The browser info context hub is not enabled in the default UI(the default browser info UI module won’t provide an option to modify the browser info but just display the browser information —the Browser Info UI module can be extended to change the default behavior)
Let us now enable the Browser Info UI Module, the ContextHub configurations can be managed through UI — refer to https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/experience-manager-65/developing/personlization/ch-configuring.html?lang=en for more details. As a quick approach, copy /libs/settings/cloudsettings/legacy to your tenant under /conf/<tenant>/settings/cloudsettings, rename may be us default. Remove the configurations that are not required.
Tools →Sites →ContextHub, Select default configuration under your tenant then select ContextHub Configuration
Select Device ContextHub UI Mode
Create a new “ContextHub UI Module(generic) inside Device
Enter the module type as contexthub.browserinfo, refer to https://experienceleague.adobe.com/docs/experience-manager-64/administering/personalization/contexthub-config.html?lang=en for more details on adding ContextHub UI Modes and Modules.
Use CRXDE, if you are facing any issue while configuring through UI.
Now modify the ContextHub path to your site root node
Now you will be able to see the browser details in ContextHub UI(as mentioned earlier you will not able to modify the browser details as the location but the UI Module can be extended/customized based on your need)
In this post, we have seen a simple scenario to Target different experiences using ContextHub and AEM targeting engine but customization can be enabled — define custom store, custom UI modules, additional rules to identify the audience, etc to enable your uses cases. The ContextHub along with the AEM targeting engine will provide limited functionalities also you may see some flickering issues while rendering the final content, use Adobe Target to enable advanced experience Targeting and A/B testing.