Creating Foreign JMS Server configurations through WLST script in Weblogic server
WebLogic JMS enables you to reference foreign (that is, external) JMS providers within a local WebLogic JNDI tree. Using the Foreign JMS Server node, you can quickly map a foreign JMS provider so that its connection factories and destinations appear in the WebLogic JNDI tree as a local JMS objects.
A Foreign JMS Server configuration can also be used to reference remote instances of WebLogic Server in another cluster or domain in the local WebLogic JNDI tree
Once the Foreign Provider is configured within Weblogic, for all practical purposes within the code — it can be called as if it was on local JNDI lookup. Weblogic will make the remote calls transparent to your code. This allows you to change your destination via configuration on the Weblogic console.
This tutorial explains the approach to configure Foreign JMS server through WLST script
WLST Script
The below WLST script help us to create a Foreign JMS server in a local server for a JMS resources running in a remote weblogic server(in different domain) but the same can be used to configure Foreign Server with external providers .
The JMS Server running on t3://localhost:7002 is configured as a Foreign JMS Server for t3://localhost:7002
The JMS clients can use the local JNDI configured in the local server to send the messages to the remote JMS server.
The same script can be modified to create a Foreign JNDI Server for other JMS providers, some of the important remote server properties to be modified is remoteDestinationJNDI, remoteConnectionFactoryJNDI, remoteConnectionURL, initialJNDIContextFactory, remoteUserName and remotePassword
ConfigureForeignJMSServer.properties
adminUserName=weblogic adminUserPassword=weblogic1 adminServerHost=localhost adminServerPort=7001foreignJMSModuleName=BAMForeginJMSResource foreignJMSServerName=BAMForeignJMSServer localConnectionFactoryJNDI=jms/BAMMonitoringConnectionfactory1 remoteConnectionFactoryJNDI=jms/BAMMonitoringConnectionfactory1 localDestinationJNDI=jms/BAMMonitoringQueue1 remoteDestinationJNDI=jms/BAMMonitoringQueue1remoteConnectionURL=t3://localhost:7002 initialJNDIContextFactory= weblogic.jndi.WLInitialContextFactory remoteUserName=weblogic remotePassword=welcome1
ConfigureForeignJMSServer.py
from java.io import FileInputStreampropInputStream = FileInputStream("ConfigureForeignJMSServer.properties") configProps = Properties() configProps.load(propInputStream)connect(configProps.get("adminUserName"),configProps.get("adminUserPassword"), 't3://'+configProps.get("adminServerHost")+':'+configProps.get("adminServerPort"))foreignJMSModuleName=configProps.get("foreignJMSModuleName") foreignJMSServerName=configProps.get("foreignJMSServerName") localConnectionFactoryJNDI=configProps.get("localConnectionFactoryJNDI") localDestinationJNDI=configProps.get("localDestinationJNDI")remoteDestinationJNDI=configProps.get("remoteDestinationJNDI") remoteConnectionFactoryJNDI=configProps.get("remoteConnectionFactoryJNDI")remoteConnectionURL=configProps.get("remoteConnectionURL") initialJNDIContextFactory=configProps.get("initialJNDIContextFactory") remoteUserName=configProps.get("remoteUserName") remotePassword=configProps.get("remotePassword")edit() startEdit()cd('/') cmo.createJMSSystemResource(foreignJMSModuleName)cd('/SystemResources/'+foreignJMSModuleName) set('Targets',jarray.array([ObjectName('com.bea:Name=AdminServer,Type=Server')], ObjectName))cd('/JMSSystemResources/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/JMSResource/'+foreignJMSModuleName) cmo.createForeignServer(foreignJMSServerName)cd('/JMSSystemResources/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/JMSResource/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/ForeignServers/'+foreignJMSServerName) cmo.setDefaultTargetingEnabled(true)cmo.setJNDIPropertiesCredential(remotePassword)cmo.setInitialContextFactory(initialJNDIContextFactory) cmo.setConnectionURL(remoteConnectionURL) cmo.createJNDIProperty('java.naming.security.principal')cd('/JMSSystemResources/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/JMSResource/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/ForeignServers/'+foreignJMSServerName+'/JNDIProperties/java.naming.security.principal') cmo.setValue(remoteUserName)cd('/JMSSystemResources/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/JMSResource/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/ForeignServers/'+foreignJMSServerName)cmo.createForeignConnectionFactory('ForeignJMSConnectionFactory')cd('/JMSSystemResources/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/JMSResource/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/ForeignServers/'+foreignJMSServerName+'/ForeignConnectionFactories/ForeignJMSConnectionFactory') cmo.setLocalJNDIName(localConnectionFactoryJNDI) cmo.setRemoteJNDIName(remoteConnectionFactoryJNDI)cd('/JMSSystemResources/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/JMSResource/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/ForeignServers/'+foreignJMSServerName) cmo.createForeignDestination('ForeignJMSDestination')cd('/JMSSystemResources/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/JMSResource/'+foreignJMSModuleName+'/ForeignServers/'+foreignJMSServerName+'/ForeignDestinations/ForeignJMSDestination') cmo.setLocalJNDIName(localDestinationJNDI) cmo.setRemoteJNDIName(remoteDestinationJNDI)activate()
Script
https://github.com/techforum-repo/youttubedata/tree/master/scripts/wlst/ConfigureForeignJMSServer
Before executing the script, change the configurations as required.
Execute the script — <<Oracle_Home>>\oracle_common\common\bin\wlst.cmd ConfigureForeignJMSServer.py
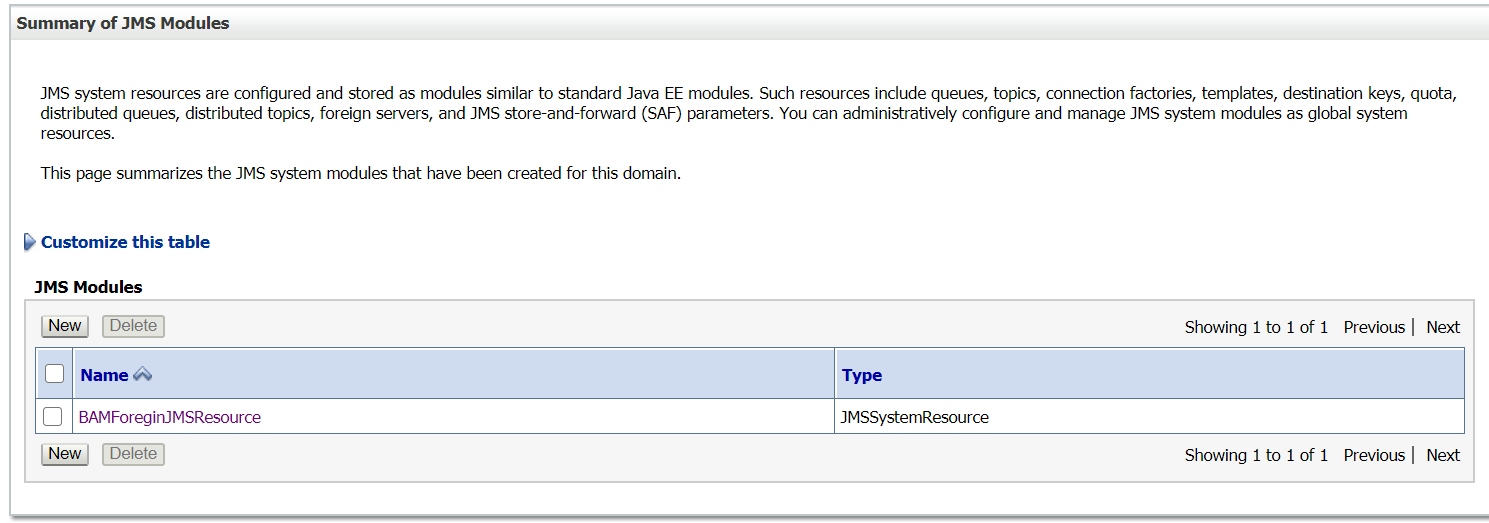
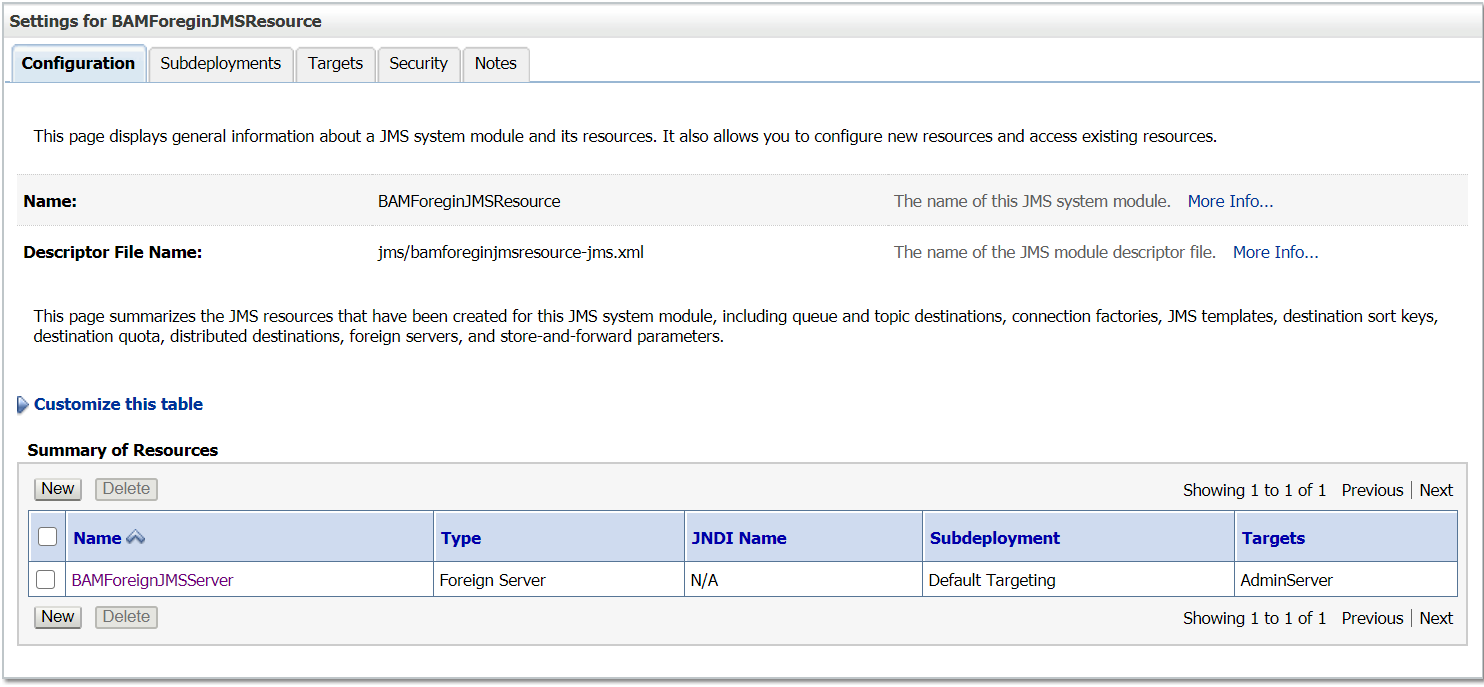
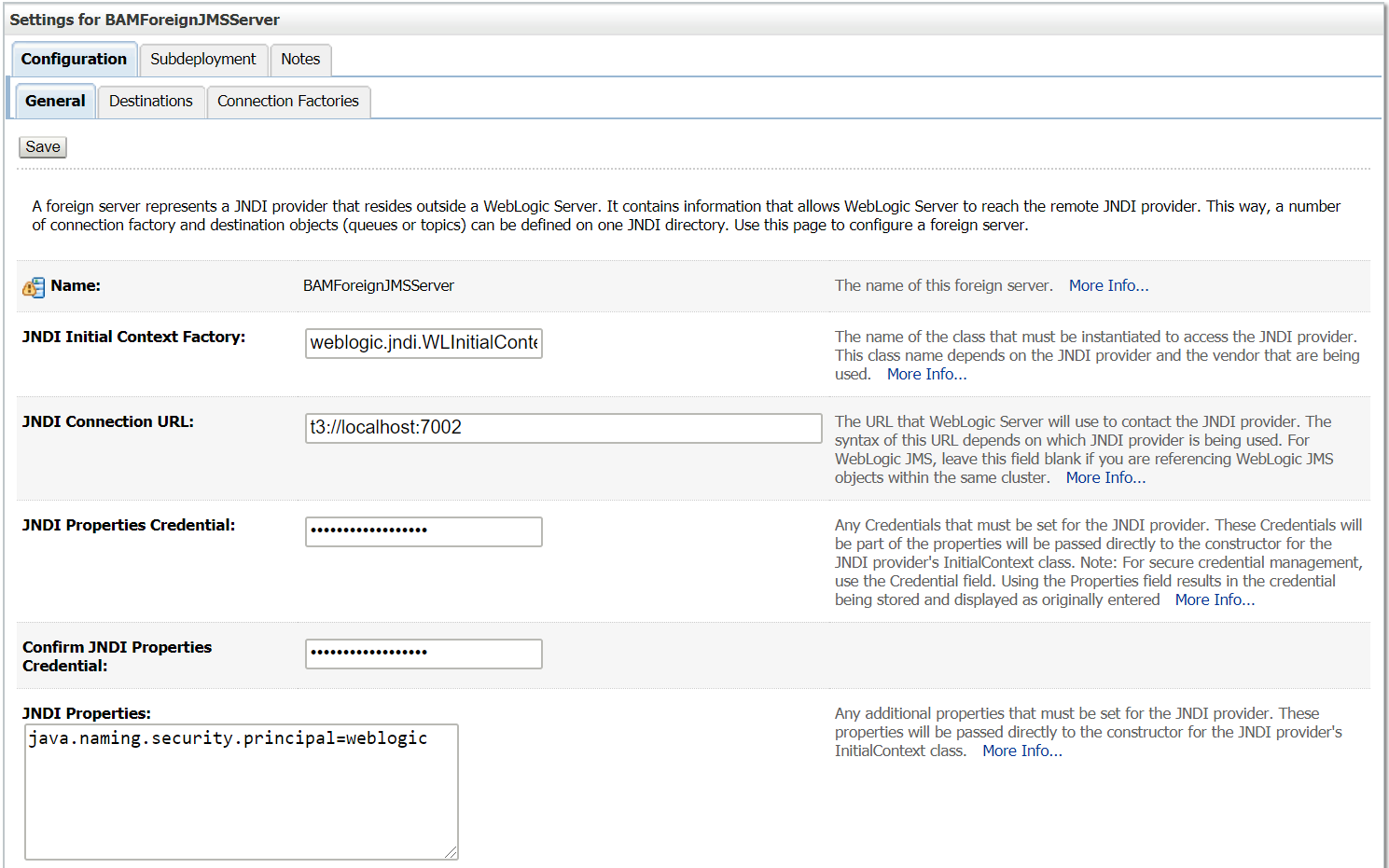
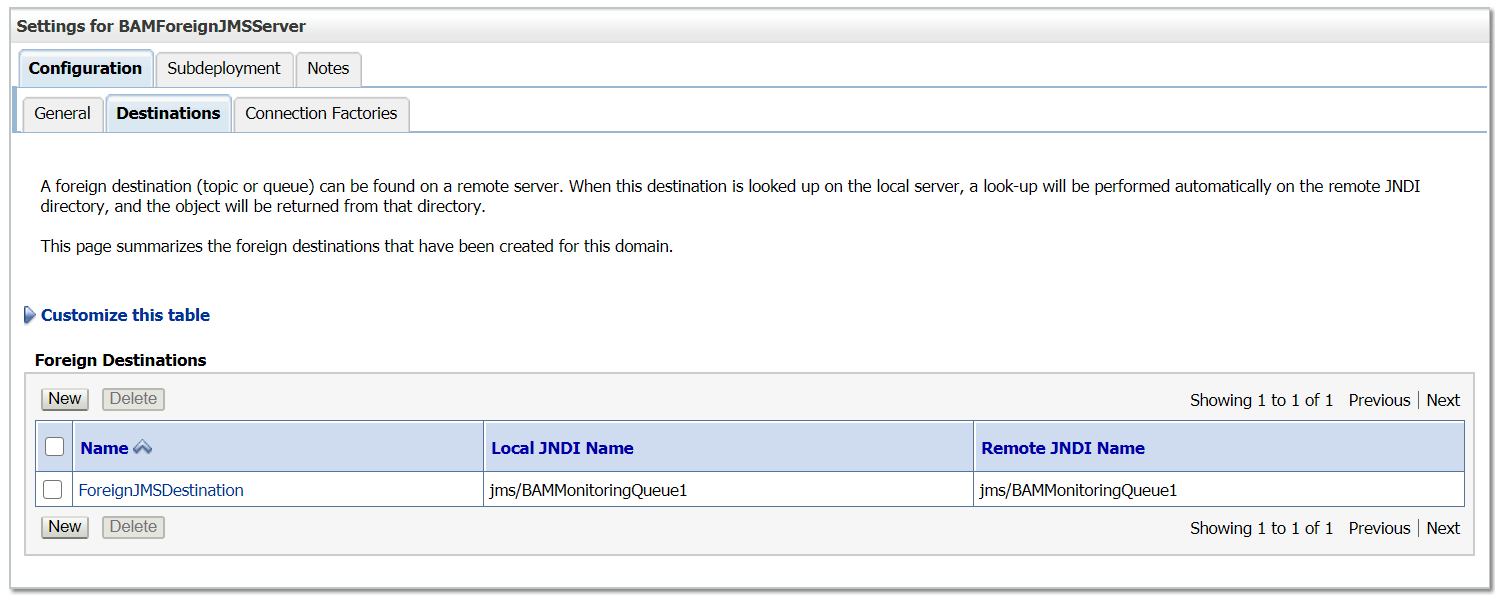
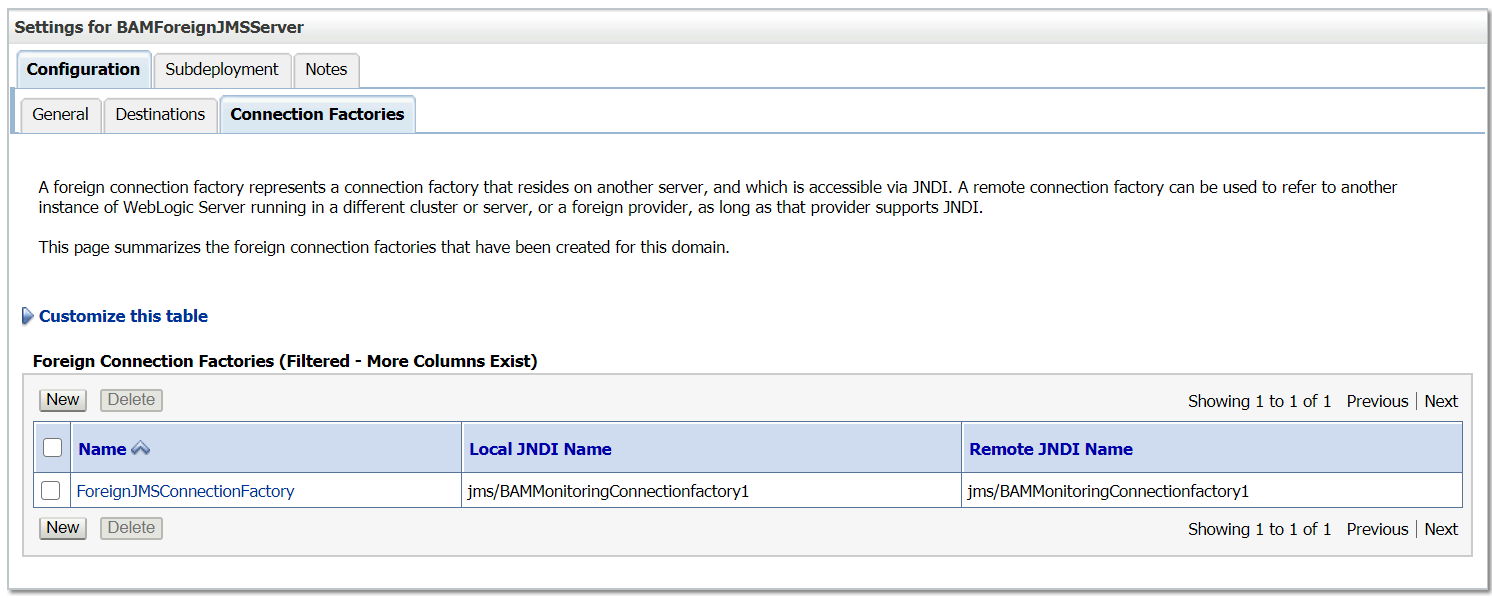
Now the foreign JMS server is configured and ready for use — the messages can be send/receive through local JNDI’s , Weblogic server internally communicate to the remote server. The foreign JMS server configuration helps as to abstract the remote server details from clients, the remote server implementations can be changed any time without impacting the clients
Your content gives readers things to think about in an interesting way.
ReplyDelete